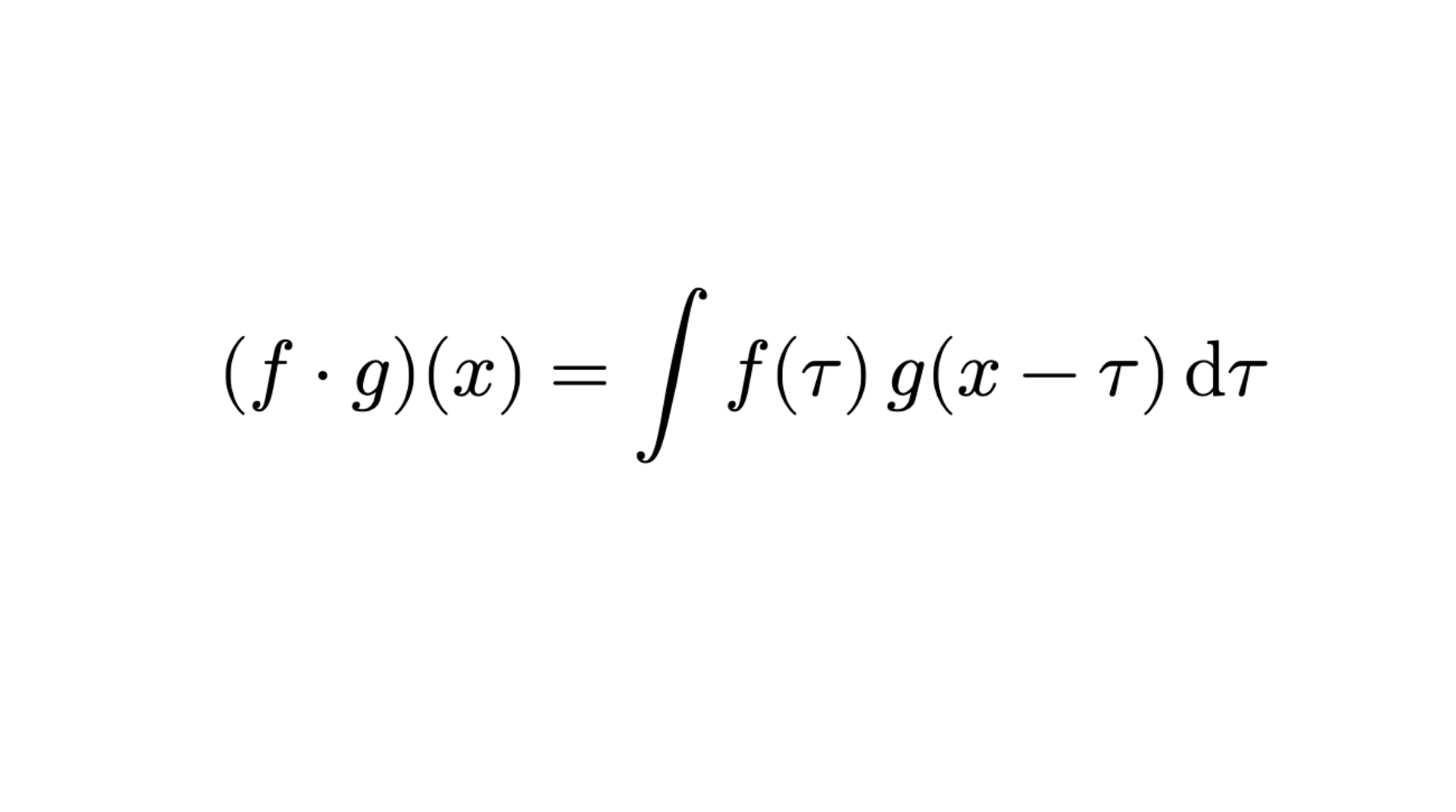Theoretical Study on Biological Phase Transition Process
Theoretical Study on Biological Phase Transition Process and Its Physicochemical Properties
Abstract
In this subject, the coarse-grained model is used to model the dynamic properties of protein beta-folded sheets. Based on the slab method, the molecular dynamics software LAMMPS is used for computer simulation, and Mathematica is used for data processing and analysis. Liquid phase separation behavior and the relationship between fundamental physicochemical parameters and the microscopic forces between monomers are studied. The results show that the coordination force between molecules is the key factor leading to the liquid-liquid phase separation, and it is found that the critical viscosity coefficient has a non-monotonic relationship with temperature.
Keywords: Biological phase transitions, coarse-grained models, liquid-liquid phase separation, slab methods, LAMMPS, Mathematica