C++高级编程
针对C++泛型编程和STL,探讨C++更深层的使用。
1. 模板
1.1 模板的概念
模板就是建立通用的模具,大大提高复用性
模板的特点:
- 模板不可以直接使用,它只是一个框架。
- 模板不是万能的。
泛型编程主要就是利用模板,C++提供两种模板,函数模板和类模板。
1.2 函数模板
1.2.1 函数模板的语法
函数模板作用:
建立一个通用函数,其函数返回值类型和形参类型可以不具体制定,用一个虚拟的类型来代表。
语法:
1template<typename T>2函数声明或定义解释:
template:声明创建模板
typename:表明其后面的符号是一种数据类型,可以用class代替
T:通用的数据类型,名称可以替换,通常为大写字母
示例如下:
x1//交换整型函数2void swapInt(int& a, int& b)3{4 int temp = a;5 a = b;6 b = temp;7}8
9//交换浮点型函数10void swapDouble(double& a, double& b)11{12 double temp = a;13 a = b;14 b = temp;15}16
17//利用模板提供通用的交换函数18template<typename T>19void mySwap(T& a, T& b)20{21 T temp = a;22 a = b;23 b = temp;24}25
26void test01()27{28 int a = 10;29 int b = 20;30 31 //swapInt(a, b);32
33 //利用模板实现交换34 //1.自动类型推导35 mySwap(a, b);36
37 //2.显示指定类型38 mySwap<int>(a, b);39
40 cout << "a = " << a << endl;41 cout << "b = " << b << endl;42
43}44
45int main()46{47 test01();48
49 system("pause");50 return 0;51}总结:
- 函数模板利用关键字 template
- 使用函数模板有两种方式:自动类型推导、显示指定类型
- 模板的目的是为了提高复用性,将类型参数化
1.2.2 函数模板注意事项
注意事项:
- 自动类型推导,必须推导出一致的数据类型T,才可以使用
- 模板必须要确定出T的数据类型,才可以使用
示例如下:
xxxxxxxxxx421//利用模板提供通用的交换函数2template<class T>3void mySwap(T& a, T& b)4{5 T temp = a;6 a = b;7 b = temp;8}9
10// 1.自动类型推导,必须推导出一致的数据类型T,才可以使用11void test01()12{13 int a = 10;14 int b = 20;15 char c = 'c';16
17 mySwap(a, b); // 正确,可以推导出一致的T18 //mySwap(a, c); // 错误,推导不出一致的T类型19}20
21
22// 2.模板必须要确定出T的数据类型,才可以使用23template<class T>24void func()25{26 cout << "func 调用" << endl;27}28
29void test02()30{31 //func(); //错误,模板不能独立使用,必须确定出T的类型32 func<int>(); //只能利用显示指定类型的方式,给T一个类型,才可以使用该模板33}34
35int main()36{37 test01();38 test02();39
40 system("pause");41 return 0;42}总结:使用模板时必须确定出通用数据类型T,并且能够推导出一致的类型。
1.2.3 函数模板的案例
案例描述:
- 利用函数模板封装一个排序的函数,可以对不同数据类型数组进行排序
- 排序规则从大到小,排序算法为选择排序法
- 分别利用char数组和int数组进行测试
示例如下:
xxxxxxxxxx651//交换的函数模板2template<typename T>3void mySwap(T &a, T &b)4{5 T temp = a;6 a = b;7 b = temp;8}9
10template<class T> // 也可以替换成typename11//利用选择排序,进行对数组从大到小的排序12void mySort(T arr[], int len)13{14 for (int i=0; i<len; i++)15 {16 int max = i; //最大数的下标17 for (int j=i+1; j<len; j++)18 {19 if (arr[max] < arr[j])20 {21 max = j;22 }23 }24 if (max != i) //如果最大数的下标不是i,交换两者25 {26 mySwap(arr[max], arr[i]);27 }28 }29}30
31//打印数组的函数模板32template<typename T>33void printArray(T arr[], int len) {34
35 for (int i=0; i<len; i++) {36 cout << arr[i] << " ";37 }38 cout << endl;39}40void test01()41{42 //测试char数组43 char charArr[] = "bdcfeagh";44 int num = sizeof(charArr) / sizeof(char);45 mySort(charArr, num);46 printArray(charArr, num);47}48
49void test02()50{51 //测试int数组52 int intArr[] = { 7, 5, 8, 1, 3, 9, 2, 4, 6 };53 int num = sizeof(intArr) / sizeof(int);54 mySort(intArr, num);55 printArray(intArr, num);56}57
58int main()59{60 test01();61 test02();62
63 system("pause");64 return 0;65}总结:模板可以提高代码复用,需要熟练掌握
1.2.4 普通函数与函数模板的区别
普通函数与函数模板区别:
- 普通函数调用时可以发生自动类型转换(隐式类型转换)
- 函数模板调用时,如果利用自动类型推导,不会发生隐式类型转换
- 如果利用显示指定类型的方式,可以发生隐式类型转换
示例如下:
xxxxxxxxxx341//普通函数2int myAdd01(int a, int b)3{4 return a + b;5}6
7//函数模板8template<class T>9T myAdd02(T a, T b) 10{11 return a + b;12}13
14//使用函数模板时,如果用自动类型推导,不会发生自动类型转换,即隐式类型转换15void test01()16{17 int a = 10;18 int b = 20;19 char c = 'c';20 21 cout << myAdd01(a,c) << endl; //正确,将char类型的'c'隐式转换为int类型'c'对应ASCII码9922
23 //myAdd02(a, c); //报错,使用自动类型推导时,不会发生隐式类型转换24
25 myAdd02<int>(a, c); //正确,如果用显示指定类型,可以发生隐式类型转换26}27
28int main()29{30 test01();31
32 system("pause");33 return 0;34}总结:建议使用显示指定类型的方式,调用函数模板,因为可以自己确定通用类型T。
1.2.5 普通函数与函数模板的调用规则
调用规则如下:
- 如果函数模板和普通函数都可以实现,优先调用普通函数
- 可以通过空模板参数列表来强制调用函数模板
- 函数模板也可以发生重载
- 如果函数模板可以产生更好的匹配,优先调用函数模板
示例如下:
xxxxxxxxxx461//普通函数与函数模板调用规则2void myPrint(int a, int b)3{4 cout << "调用的普通函数" << endl;5}6
7template<typename T>8void myPrint(T a, T b) 9{ 10 cout << "调用的模板" << endl;11}12
13template<typename T>14void myPrint(T a, T b, T c) 15{ 16 cout << "调用重载的模板" << endl; 17}18
19void test01()20{21 //1.如果函数模板和普通函数都可以实现,优先调用普通函数22 //注意:如果告诉编译器普通函数是有的,但只是声明没有实现,就会报错找不到23 int a = 10;24 int b = 20;25 myPrint(a, b); //调用普通函数26
27 //2.可以通过空模板参数列表来强制调用函数模板28 myPrint<>(a, b); //调用函数模板29
30 //3.函数模板也可以发生重载31 int c = 30;32 myPrint(a, b, c); //调用重载的函数模板33
34 //4.如果函数模板可以产生更好的匹配,优先调用函数模板35 char c1 = 'a';36 char c2 = 'b';37 myPrint(c1, c2); //调用函数模板38}39
40int main()41{42 test01();43
44 system("pause");45 return 0;46}总结:既然提供了函数模板,最好就不要提供普通函数,否则容易出现二义性。
1.2.6 模板的局限性
局限性:模板的通用性并不是万能的。
例如:
xxxxxxxxxx51template<class T>2void f(T a, T b)3{ 4 a = b;5}在上述代码中提供的赋值操作,如果传入的a和b是一个数组,就无法实现了。
再例如:
xxxxxxxxxx51template<class T>2void f(T a, T b)3{ 4 if(a > b) { ... }5}在上述代码中,如果T的数据类型传入的是像Person这样的自定义数据类型,也无法正常运行。
因此C++为了解决这种问题,提供模板的具体化,可以为这些特定的类型提供具体化的模板。
示例如下:
xxxxxxxxxx861using namespace std;3
4
6class Person7{8public:9 Person(string name, int age)10 {11 this->m_Name = name;12 this->m_Age = age;13 }14 string m_Name;15 int m_Age;16};17
18//普通函数模板19template<class T>20bool myCompare(T& a, T& b)21{22 if (a == b)23 {24 return true;25 }26 else27 {28 return false;29 }30}31
32//具体化的定义以template<>开头33//具体化优先于常规模板34template<> bool myCompare(Person &p1, Person &p2)35{36 if ( p1.m_Name == p2.m_Name && p1.m_Age == p2.m_Age)37 {38 return true;39 }40 else41 {42 return false;43 }44}45
46void test01()47{48 int a = 10;49 int b = 20;50 //内置数据类型可以直接使用通用的函数模板51 bool ret = myCompare(a, b);52 if (ret)53 {54 cout << "a == b " << endl;55 }56 else57 {58 cout << "a != b " << endl;59 }60}61
62void test02()63{64 Person p1("Tom", 10);65 Person p2("Tom", 10);66 //自定义数据类型,不会调用普通的函数模板67 //可以创建具体化的Person数据类型的模板,用于特殊处理这个类型68 bool ret = myCompare(p1, p2);69 if (ret)70 {71 cout << "p1 == p2 " << endl;72 }73 else74 {75 cout << "p1 != p2 " << endl;76 }77}78
79int main()80{81 test01();82 test02();83
84 system("pause");85 return 0;86}总结:
- 利用具体化的模板,可以解决自定义类型的通用化
- 学习模板并不是为了写模板,而是在STL能够运用系统提供的模板
1.3 类模板
1.3.1 类模板语法
类模板作用:建立一个通用类,类中的成员数据类型可以不具体指定,用一个虚拟的类型来代表。
语法:
xxxxxxxxxx21template<typename T>2类解释:
template:声明创建模板
typename:表面其后面的符号是一种数据类型,可以用class代替
T:通用的数据类型,名称可以替换,通常为大写字母
示例如下:
xxxxxxxxxx351
3//类模板4template<class NameType, class AgeType> 5class Person6{7public:8 Person(NameType name, AgeType age)9 {10 this->mName = name;11 this->mAge = age;12 }13 void showPerson()14 {15 cout << "name: " << this->mName << " age: " << this->mAge << endl;16 }17public:18 NameType mName;19 AgeType mAge;20};21
22void test01()23{24 // 指定NameType为string类型,AgeType为int类型25 Person<string, int>P1("孙悟空", 999);26 P1.showPerson();27}28
29int main()30{31 test01();32
33 system("pause");34 return 0;35}总结:类模板和函数模板语法相似,在声明模板template后面加类,此类称为类模板。
1.3.2 类模板与函数模板区别
类模板与函数模板区别主要有两点:
- 类模板没有自动类型推导的使用方式
- 类模板在模板参数列表中可以有默认参数
示例如下:
xxxxxxxxxx441
3//类模板4template<class NameType, class AgeType = int> 5class Person6{7public:8 Person(NameType name, AgeType age)9 {10 this->mName = name;11 this->mAge = age;12 }13 void showPerson()14 {15 cout << "name: " << this->mName << " age: " << this->mAge << endl;16 }17public:18 NameType mName;19 AgeType mAge;20};21
22//1.类模板没有自动类型推导的使用方式23void test01()24{25 // Person p("孙悟空", 1000); //错误 类模板使用时候,不可以用自动类型推导26 Person <string ,int>p("孙悟空", 1000); //必须使用显示指定类型的方式,使用类模板27 p.showPerson();28}29
30//2.类模板在模板参数列表中可以有默认参数31void test02()32{33 Person <string> p("猪八戒", 999); //类模板中的模板参数列表 可以指定默认参数34 p.showPerson();35}36
37int main()38{39 test01();40 test02();41
42 system("pause");43 return 0;44}总结:
- 类模板使用只能用显示指定类型方式
- 类模板中的模板参数列表可以有默认参数
1.3.3 类模板中成员函数创建时机
类模板中成员函数和普通类中成员函数创建时机是有区别的:
- 普通类中的成员函数一开始就可以创建
- 类模板中的成员函数在调用时才创建
示例如下:
xxxxxxxxxx471class Person12{3public:4 void showPerson1()5 {6 cout << "Person1 show" << endl;7 }8};9
10class Person211{12public:13 void showPerson2()14 {15 cout << "Person2 show" << endl;16 }17};18
19template<class T>20class MyClass21{22public:23 T obj;24
25 //类模板中的成员函数,并不是一开始就创建的,而是在模板调用时再生成26
27 void fun1() { obj.showPerson1(); }28 void fun2() { obj.showPerson2(); }29
30};31
32void test01()33{34 MyClass<Person1> m;35 36 m.fun1();37
38 //m.fun2(); //编译会出错,说明函数调用才会去创建成员函数39}40
41int main()42{43 test01();44
45 system("pause");46 return 0;47}总结:类模板中的成员函数并不是一开始就创建的,在调用时才去创建。
1.3.4 类模板对象做函数参数
类模板实例化出的对象,向函数传参的方式,一共有三种传入方式:
- 指定传入的类型 直接显示对象的数据类型
- 参数模板化 将对象中的参数变为模板进行传递
- 整个类模板化 将这个对象类型模板化进行传递
示例如下:
xxxxxxxxxx681
3//类模板4template<class NameType, class AgeType = int> 5class Person6{7public:8 Person(NameType name, AgeType age)9 {10 this->mName = name;11 this->mAge = age;12 }13 void showPerson()14 {15 cout << "name: " << this->mName << " age: " << this->mAge << endl;16 }17public:18 NameType mName;19 AgeType mAge;20};21
22//1.指定传入的类型23void printPerson1(Person<string, int> &p) 24{25 p.showPerson();26}27void test01()28{29 Person <string, int >p("孙悟空", 100);30 printPerson1(p);31}32
33//2.参数模板化34template <class T1, class T2>35void printPerson2(Person<T1, T2>&p)36{37 p.showPerson();38 cout << "T1的类型为: " << typeid(T1).name() << endl;39 cout << "T2的类型为: " << typeid(T2).name() << endl;40}41void test02()42{43 Person <string, int >p("猪八戒", 90);44 printPerson2(p);45}46
47//3.整个类模板化48template<class T>49void printPerson3(T & p)50{51 p.showPerson();52 cout << "T的类型为: " << typeid(T).name() << endl;53}54void test03()55{56 Person <string, int >p("唐僧", 30);57 printPerson3(p);58}59
60int main()61{62 test01();63 test02();64 test03();65
66 system("pause");67 return 0;68}总结:
- 通过类模板创建的对象,可以有三种方式向函数中进行传参
- 使用比较广泛是第一种:指定传入的类型
- 第二种和第三种实际上是类模板配合函数模板,比较复杂
1.3.5 类模板与继承
当类模板碰到继承时,需要注意以下几点:
- 当子类继承的父类是一个类模板时,子类在声明的时候,要指定出父类中T的类型
- 如果不指定,编译器无法给子类分配内存,会报错
- 如果想灵活指定出父类中T的类型,子类也需变为类模板
示例如下:
xxxxxxxxxx451template<class T>2class Base3{4 T m;5};6
7//class Son:public Base //错误,c++编译需要给子类分配内存,必须知道父类中T的类型才可以向下继承8class Son :public Base<int> //必须指定一个类型9{10};11
12void test01()13{14 Son c;15}16
17//如果想灵活指定出父类中T的类型,子类也需变为类模板18template<class T1, class T2>19class Son2 :public Base<T2>20{21public:22 Son2()23 {24 cout << typeid(T1).name() << endl;25 cout << typeid(T2).name() << endl;26 }27 28public:29 T1 n;30};31
32void test02()33{34 Son2<int, char> child1;35}36
37
38int main()39{40 test01();41 test02();42
43 system("pause");44 return 0;45}总结:如果父类是类模板,子类需要指定出父类中T的数据类型。
1.3.6 类模板成员函数类外实现
示例如下:
xxxxxxxxxx411
3//类模板中成员函数类外实现4template<class T1, class T2>5class Person {6public:7 //成员函数类内声明8 Person(T1 name, T2 age);9 void showPerson();10
11public:12 T1 m_Name;13 T2 m_Age;14};15
16//构造函数 类外实现17template<class T1, class T2>18Person<T1, T2>::Person(T1 name, T2 age) {19 this->m_Name = name;20 this->m_Age = age;21}22
23//成员函数 类外实现24template<class T1, class T2>25void Person<T1, T2>::showPerson() {26 cout << "姓名: " << this->m_Name << " 年龄:" << this->m_Age << endl;27}28
29void test01()30{31 Person<string, int> p("Tom", 20);32 p.showPerson();33}34
35int main()36{37 test01();38
39 system("pause");40 return 0;41}总结:类模板中成员函数类外实现时,需要加上模板参数列表。
1.3.7 类模板分文件编写
将声明和实现写到同一个文件中,并更改后缀名为.hpp,hpp是约定的名称,并不是强制。
示例如下:
person.hpp中代码:
xxxxxxxxxx271using namespace std;4
6template<class T1, class T2>7class Person {8public:9 Person(T1 name, T2 age);10 void showPerson();11public:12 T1 m_Name;13 T2 m_Age;14};15
16//构造函数 类外实现17template<class T1, class T2>18Person<T1, T2>::Person(T1 name, T2 age) {19 this->m_Name = name;20 this->m_Age = age;21}22
23//成员函数 类外实现24template<class T1, class T2>25void Person<T1, T2>::showPerson() {26 cout << "姓名: " << this->m_Name << " 年龄:" << this->m_Age << endl;27}主函数.cpp中代码
xxxxxxxxxx181using namespace std;3
4
6void test01()7{8 Person<string, int> p("Tom", 10);9 p.showPerson();10}11
12int main()13{14 test01();15
16 system("pause");17 return 0;18}1.3.8 类模板与友元
全局函数类内实现:直接在类内声明友元并写出全局函数的实现
全局函数类外实现:需要提前让编译器知道全局函数的存在,并且全局函数用到了类模板参数,还得让这个全局函数知道有这么个类模板。
示例如下:
全局函数类内实现
xxxxxxxxxx391
3template<class T1, class T2>4class Person5{6 //1.全局函数配合友元 类内实现7 friend void printPerson(Person<T1, T2> & p)8 {9 cout << "姓名: " << p.m_Name << " 年龄:" << p.m_Age << endl;10 }11
12
13public:14 Person(T1 name, T2 age)15 {16 this->m_Name = name;17 this->m_Age = age;18 }19
20private:21 T1 m_Name;22 T2 m_Age;23
24};25
26//1.全局函数在类内实现27void test01()28{29 Person <string, int >p("Tom", 20);30 printPerson(p);31}32
33int main()34{35 test01();36 37 system("pause");38 return 0;39}全局函数类外实现
xxxxxxxxxx441
3template<class T1, class T2> class Person;4
5//需要提前让编译器知道全局函数的存在,但是全局函数用到了类模板参数,还得让这个全局函数知道有这么个类模板。故上面还需对类模板进行声明6template<class T1, class T2>7void printPerson2(Person<T1, T2> & p)8{9 cout << "类外实现 ---- 姓名: " << p.m_Name << " 年龄:" << p.m_Age << endl;10}11
12template<class T1, class T2>13class Person14{15 //2.全局函数配合友元 类外实现16 friend void printPerson2<>(Person<T1, T2> & p);17
18public:19 Person(T1 name, T2 age)20 {21 this->m_Name = name;22 this->m_Age = age;23 }24
25private:26 T1 m_Name;27 T2 m_Age;28
29};30
31//2.全局函数在类外实现32void test02()33{34 Person <string, int >p("Jerry", 30);35 printPerson2(p);36}37
38int main()39{ 40 test02();41
42 system("pause");43 return 0;44}总结:建议全局函数做类内实现,用法简单,而且编译器可以直接识别。
1.3.9 类模板案例(案例比较综合,含金量比较高)
案例描述: 实现一个通用的数组类,要求如下:
- 可以对内置数据类型以及自定义数据类型的数据进行存储
- 将数组中的数据存储到堆区
- 构造函数中可以传入数组的容量
- 提供对应的拷贝构造函数以及operator=防止浅拷贝问题
- 提供尾插法和尾删法对数组中的数据进行增加和删除
- 可以通过下标的方式访问数组中的元素
- 可以获取数组中当前元素个数和数组的容量
示例如下:
myArray.hpp中代码
xxxxxxxxxx1081using namespace std;4
5template<class T>6class MyArray7{8public:9 10 //构造函数11 MyArray(int capacity)12 {13 this->m_Capacity = capacity;14 this->m_Size = 0;15 pAddress = new T[this->m_Capacity];16 }17
18 //拷贝构造19 MyArray(const MyArray & arr)20 {21 this->m_Capacity = arr.m_Capacity;22 this->m_Size = arr.m_Size;23 this->pAddress = new T[this->m_Capacity];24 for (int i = 0; i < this->m_Size; i++)25 {26 //如果T为自定义的对象,而且还包含指针,必须需要重载 = 操作符,因为自定义的对象不能直接赋值27 //普通类型可以直接 = 但是指针类型需要深拷贝28 this->pAddress[i] = arr.pAddress[i];29 }30 }31
32 //重载=操作符 防止浅拷贝问题33 MyArray& operator=(const MyArray& myarray) 34 {35
36 if (this->pAddress != NULL) {37 delete[] this->pAddress;38 this->m_Capacity = 0;39 this->m_Size = 0;40 }41
42 this->m_Capacity = myarray.m_Capacity;43 this->m_Size = myarray.m_Size;44 this->pAddress = new T[this->m_Capacity];45 for (int i = 0; i < this->m_Size; i++) {46 this->pAddress[i] = myarray[i];47 }48 return *this;49 }50
51 //重载[] 操作符 arr[0] 这样才能用下标进行访问52 T& operator [](int index)53 {54 return this->pAddress[index]; //不考虑越界,用户自己去处理55 }56
57 //尾插法58 void Push_back(const T & val)59 {60 if (this->m_Capacity == this->m_Size)61 {62 //已经满了63 return;64 }65 this->pAddress[this->m_Size] = val;66 this->m_Size++;67 }68
69 //尾删法70 void Pop_back()71 {72 if (this->m_Size == 0)73 {74 return;75 }76 this->m_Size--;77 }78
79 //获取数组容量80 int getCapacity()81 {82 return this->m_Capacity;83 }84
85 //获取数组大小86 int getSize()87 {88 return this->m_Size;89 }90
91
92 //析构93 ~MyArray()94 {95 if (this->pAddress != NULL)96 {97 delete[] this->pAddress;98 this->pAddress = NULL;99 this->m_Capacity = 0;100 this->m_Size = 0;101 }102 }103
104private:105 T * pAddress; //指向一块堆区空间,这个空间存储真正的数据106 int m_Capacity; //容量107 int m_Size; // 大小108};
类模板案例—数组类封装.cpp中
xxxxxxxxxx921
4void printIntArray(MyArray<int>& arr) 5{6 for (int i = 0; i < arr.getSize(); i++) 7 {8 cout << arr[i] << " ";9 }10 cout << endl;11}12
13//测试内置数据类型14void test01()15{16 MyArray<int> array1(10);17 for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++)18 {19 array1.Push_back(i);20 }21 cout << "array1打印输出:" << endl;22 printIntArray(array1);23 cout << "array1的大小:" << array1.getSize() << endl;24 cout << "array1的容量:" << array1.getCapacity() << endl;25
26 cout << "--------------------------" << endl;27
28 MyArray<int> array2(array1);29 array2.Pop_back();30 cout << "array2打印输出:" << endl;31 printIntArray(array2);32 cout << "array2的大小:" << array2.getSize() << endl;33 cout << "array2的容量:" << array2.getCapacity() << endl;34}35
36//测试自定义数据类型37class Person 38{39public:40 Person() {} 41 Person(string name, int age) 42 {43 this->m_Name = name;44 this->m_Age = age;45 }46public:47 string m_Name;48 int m_Age;49};50
51void printPersonArray(MyArray<Person>& personArr)52{53 for (int i = 0; i < personArr.getSize(); i++) {54 cout << "姓名:" << personArr[i].m_Name << " 年龄: " << personArr[i].m_Age << endl;55 }56
57}58
59void test02()60{61 //创建数组62 MyArray<Person> pArray(10);63 Person p1("孙悟空", 30);64 Person p2("韩信", 20);65 Person p3("妲己", 18);66 Person p4("王昭君", 15);67 Person p5("赵云", 24);68
69 //插入数据70 pArray.Push_back(p1);71 pArray.Push_back(p2);72 pArray.Push_back(p3);73 pArray.Push_back(p4);74 pArray.Push_back(p5);75
76 printPersonArray(pArray);77
78 cout << "pArray的大小:" << pArray.getSize() << endl;79 cout << "pArray的容量:" << pArray.getCapacity() << endl;80
81}82
83int main() 84{85
86 //test01();87 88 test02();89
90 system("pause");91 return 0;92}总结:能够利用所学知识点实现通用的数组,这个案例综合性较强,涉及到核心编程部分的构造(普通构造和拷贝构造)、析构、运算符重载(=和[ ])以及高级编程部分的类模板。在拷贝构造和=运算符重载的过程中要注意深拷贝,防止堆区内存重复释放。
2.STL初识
2.1 STL的诞生
- 长久以来,软件界一直希望建立一种可重复利用的东西
- C++的面向对象和泛型编程思想,目的就是复用性的提升
- 大多情况下,数据结构和算法都未能有一套标准,导致被迫从事大量重复工作
- 为了建立数据结构和算法的一套标准,诞生了STL
2.2 STL基本概念
- STL(Standard Template Library,标准模板库)
- STL 从广义上分为:容器(container) 算法(algorithm) 迭代器(iterator)
- 容器和算法之间通过迭代器进行无缝连接。
- STL 几乎所有的代码都采用了模板类或者模板函数
2.3 STL六大组件
STL大体分为六大组件,分别是:容器、算法、迭代器、仿函数、适配器(配接器)、空间配置器
- 容器:各种数据结构,如vector、list、deque、set、map等,用来存放数据。
- 算法:各种常用的算法,如sort、find、copy、for_each等
- 迭代器:扮演了容器与算法之间的胶合剂。
- 仿函数:行为类似函数,可作为算法的某种策略。
- 适配器:一种用来修饰容器或者仿函数或迭代器接口的东西。
- 空间配置器:负责空间的配置与管理。
2.4 STL中容器、算法、迭代器
容器:置物之所也
STL容器就是将运用最广泛的一些数据结构实现出来
常用的数据结构:数组、链表、树、栈、队列、集合、映射表等
这些容器分为序列式容器和关联式容器两种:
序列式容器:强调值的排序,序列式容器中的每个元素均有固定的位置。 关联式容器:二叉树结构,各元素之间没有严格的物理上的顺序关系。
算法:问题之解法也
有限的步骤,解决逻辑或数学上的问题,这一门学科我们叫做算法(Algorithms)
算法分为:质变算法和非质变算法。
质变算法:是指运算过程中会更改区间内的元素的内容。例如替换,删除等等
非质变算法:是指运算过程中不会更改区间内的元素内容。例如查找、计数、遍历、寻找极值等等
迭代器:容器和算法之间粘合剂
提供一种方法,使之能够依序寻访某个容器所含的各个元素,而又无需暴露该容器的内部表示方式。
每个容器都有自己专属的迭代器
迭代器使用非常类似于指针,初学阶段我们可以先理解迭代器为指针
迭代器种类:
| 种类 | 功能 | 支持运算 |
|---|---|---|
| 输入迭代器 | 对数据的只读访问 | 只读,支持++、==、!= |
| 输出迭代器 | 对数据的只写访问 | 只写,支持++ |
| 前向迭代器 | 读写操作,并能向前推进迭代器 | 读写,支持++、==、!= |
| 双向迭代器 | 读写操作,并能向前和向后操作 | 读写,支持++、-- |
| 随机访问迭代器 | 读写操作,可以以跳跃的方式访问任意数据,功能最强的迭代器 | 读写,支持++、--、[n]、-n、<、<=、>、>= |
常用的容器中迭代器种类为双向迭代器,和随机访问迭代器。
2.5 容器算法迭代器初识
了解STL中容器、算法、迭代器概念之后,我们利用代码感受STL的魅力
STL中最常用的容器为Vector,可以理解为数组,下面我们将学习如何向这个容器中插入数据、并遍历这个容器。
2.5.1 vector存放内置数据类型
容器: vector
算法: for_each
迭代器: vector<int>::iterator
示例如下:
xxxxxxxxxx521
4void MyPrint(int val)5{6 cout << val << endl;7}8
9void test01() 10{11
12 //创建vector容器对象,并且通过模板参数指定容器中存放的数据的类型13 vector<int> v;14 15 //向容器中放数据16 v.push_back(10);17 v.push_back(20);18 v.push_back(30);19 v.push_back(40);20
21 //每一个容器都有自己的迭代器,迭代器是用来遍历容器中的元素22 //v.begin()返回迭代器,这个迭代器指向容器中第一个数据23 //v.end()返回迭代器,这个迭代器指向容器元素的最后一个元素的下一个位置24 //vector<int>::iterator 拿到vector<int>这种容器的迭代器类型25
26 vector<int>::iterator pBegin = v.begin();27 vector<int>::iterator pEnd = v.end();28
29 //第一种遍历方式:30 while (pBegin != pEnd) {31 cout << *pBegin << endl;32 pBegin++;33 }34
35 //第二种遍历方式:36 for (vector<int>::iterator it = v.begin(); it != v.end(); it++) 37 {38 cout << *it << endl;39 }40
41 //第三种遍历方式:42 //使用STL提供标准遍历算法 要加上头文件 algorithm43 for_each(v.begin(), v.end(), MyPrint); //MyPrint为我们定义的函数44}45
46int main() 47{48 test01();49
50 system("pause");51 return 0;52}2.5.2 Vector存放自定义数据类型
vector中存放自定义数据类型Person,并打印输出。示例如下:
xxxxxxxxxx761
4//自定义数据类型5class Person 6{7public:8 Person(string name, int age) 9 {10 mName = name;11 mAge = age;12 }13public:14 string mName;15 int mAge;16};17
18//存放对象19void test01() 20{21 vector<Person> v;22
23 //创建数据24 Person p1("aaa", 10);25 Person p2("bbb", 20);26 Person p3("ccc", 30);27 Person p4("ddd", 40);28 Person p5("eee", 50);29
30 v.push_back(p1);31 v.push_back(p2);32 v.push_back(p3);33 v.push_back(p4);34 v.push_back(p5);35
36 for (vector<Person>::iterator it = v.begin(); it != v.end(); it++) 37 {38 cout << "Name:" << (*it).mName << " Age:" << (*it).mAge << endl;39
40 }41}42
43//放对象指针44void test02() {45
46 vector<Person*> v;47
48 //创建数据49 Person p1("aaa", 10);50 Person p2("bbb", 20);51 Person p3("ccc", 30);52 Person p4("ddd", 40);53 Person p5("eee", 50);54
55 v.push_back(&p1);56 v.push_back(&p2);57 v.push_back(&p3);58 v.push_back(&p4);59 v.push_back(&p5);60
61 for (vector<Person*>::iterator it = v.begin(); it != v.end(); it++) 62 {63 Person * p = (*it);64 cout << "Name:" << p->mName << " Age:" << (*it)->mAge << endl;65 }66}67
68
69int main() 70{71 test01();72 test02();73
74 system("pause");75 return 0;76}2.5.3 Vector容器嵌套容器
容器中嵌套容器,我们将所有数据进行遍历输出。示例如下:
xxxxxxxxxx481
3//容器嵌套容器4void test01() 5{6 //定义大容器7 vector< vector<int> > v;8
9 //定义小容器10 vector<int> v1;11 vector<int> v2;12 vector<int> v3;13 vector<int> v4;14
15 //往小容器里面放东西16 for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) 17 {18 v1.push_back(i + 1);19 v2.push_back(i + 2);20 v3.push_back(i + 3);21 v4.push_back(i + 4);22 }23
24 //将小容器放入大容器中25 v.push_back(v1);26 v.push_back(v2);27 v.push_back(v3);28 v.push_back(v4);29
30 //遍历31 for (vector<vector<int>>::iterator it = v.begin(); it != v.end(); it++) 32 {33 for (vector<int>::iterator vit = (*it).begin(); vit != (*it).end(); vit++) 34 {35 cout << *vit << " ";36 }37 cout << endl;38 }39
40}41
42int main() 43{44 test01();45
46 system("pause");47 return 0;48}3 STL- 常用容器
3.1 string容器
3.1.1 string基本概念
本质:string是C++风格的字符串,而string本质上是一个类
string和char * 区别:
- char * 是一个指针
- string是一个类,类内部封装了char*,管理这个字符串,是一个char*型的容器。
特点:
string 类内部封装了很多成员方法
例如:查找find、拷贝copy、删除delete、 替换replace、插入insert
string管理char*所分配的内存,不用担心复制越界和取值越界等,由类内部进行负责
3.1.2 string构造函数
构造函数原型:
string();创建一个空的字符串 例如:string str;string(const char* s);使用字符串s初始化string(const string& str);使用一个string对象初始化另一个string对象string(int n, char c);使用n个字符c初始化
示例如下:
xxxxxxxxxx261
3//string构造4void test01()5{6 string s1; //创建空字符串,调用无参构造函数7 cout << "str1 = " << s1 << endl;8
9 const char* str = "hello world";10 string s2(str); //把char*转换成了string11 cout << "str2 = " << s2 << endl;12
13 string s3(s2); //调用拷贝构造函数14 cout << "str3 = " << s3 << endl;15
16 string s4(10, 'a'); //使用n个字符c初始化 17 cout << "str4 = " << s4 << endl;18}19
20int main() 21{22 test01();23
24 system("pause");25 return 0;26}总结:string的多种构造方式没有可比性,灵活使用即可。
3.1.3 string赋值操作
功能描述:给string字符串进行赋值。
赋值的函数原型:
string& operator=(const char* s);char*类型字符串 赋值给当前的字符串string& operator=(const string &s);把字符串s赋给当前的字符串string& operator=(char c);字符赋值给当前的字符串string& assign(const char *s);把字符串s赋给当前的字符串string& assign(const char *s, int n);把字符串s的前n个字符赋给当前的字符串string& assign(const string &s);把字符串s赋给当前字符串string& assign(int n, char c);用n个字符c赋给当前字符串
示例如下:
xxxxxxxxxx391//string赋值操作2void test01()3{4 string str1;5 str1 = "hello world";6 cout << "str1 = " << str1 << endl;7
8 string str2;9 str2 = str1;10 cout << "str2 = " << str2 << endl;11
12 string str3;13 str3 = 'a';14 cout << "str3 = " << str3 << endl;15
16 string str4;17 str4.assign("hello c++");18 cout << "str4 = " << str4 << endl;19
20 string str5;21 str5.assign("hello c++",5);22 cout << "str5 = " << str5 << endl;23
24 string str6;25 str6.assign(str5);26 cout << "str6 = " << str6 << endl;27
28 string str7;29 str7.assign(5, 'x');30 cout << "str7 = " << str7 << endl;31}32
33int main() 34{35 test01();36
37 system("pause");38 return 0;39}总结:string的赋值方式很多,operator= 这种方式是比较常用的。
3.1.4 string字符串拼接
功能描述:实现在字符串末尾拼接字符串
函数原型:
string& operator+=(const char* str);重载+=操作符string& operator+=(const char c);重载+=操作符string& operator+=(const string& str);重载+=操作符string& append(const char *s);把字符串s连接到当前字符串结尾string& append(const char *s, int n);把字符串s的前n个字符连接到当前字符串结尾string& append(const string &s);同operator+=(const string& str)string& append(const string &s, int pos, int n);字符串s中从pos开始的n个字符连接到字符串结尾
示例如下:
xxxxxxxxxx311//字符串拼接2void test01()3{4 string str1 = "我";5 str1 += "爱玩游戏";6 cout << "str1 = " << str1 << endl;7 8 str1 += ':';9 cout << "str1 = " << str1 << endl;10
11 string str2 = "LOL DNF";12 str1 += str2;13 cout << "str1 = " << str1 << endl;14
15 string str3 = "I";16 str3.append(" love ");17 18 str3.append("game abcde", 4);19 20 str3.append(str2);21 22 str3.append(str2, 4, 3); //从下标4位置开始,截取3个字符,拼接到字符串末尾23 cout << "str3 = " << str3 << endl;24}25int main() 26{27 test01();28 29 system("pause");30 return 0;31}总结:字符串拼接的重载版本很多,记住几种即可。
3.1.5 string查找和替换
功能描述:
- 查找:查找指定字符串是否存在
- 替换:在指定的位置替换字符串
函数原型:
int find(const string& str, int pos = 0) const;查找str第一次出现位置,从pos开始查找int find(const char* s, int pos = 0) const;查找s第一次出现位置,从pos开始查找int find(const char* s, int pos, int n) const;从pos位置查找s的前n个字符第一次位置int find(const char c, int pos = 0) const;查找字符c第一次出现位置int rfind(const string& str, int pos = npos) const;查找str最后一次位置,从pos开始查找int rfind(const char* s, int pos = npos) const;查找s最后一次出现位置,从pos开始查找int rfind(const char* s, int pos, int n) const;从pos查找s的前n个字符最后一次位置int rfind(const char c, int pos = 0) const;查找字符c最后一次出现位置string& replace(int pos, int n, const string& str);替换从pos开始n个字符为字符串strstring& replace(int pos, int n,const char* s);替换从pos开始的n个字符为字符串s
示例如下:
xxxxxxxxxx401//查找和替换2void test01()3{4 //查找5 string str1 = "abcdefgde";6
7 int pos = str1.find("de");8 9 if (pos == -1)10 {11 cout << "未找到" << endl;12 }13 else14 {15 cout << "pos = " << pos << endl;16 }17 18
19 pos = str1.rfind("de");20 cout << "pos = " << pos << endl;21
22}23
24void test02()25{26 //替换27 string str1 = "abcdefgde";28 str1.replace(1, 3, "1111");29
30 cout << "str1 = " << str1 << endl;31}32
33int main() 34{35 test01();36 test02();37
38 system("pause");39 return 0;40}总结:
- find查找是从左往后,rfind从右往左
- find找到字符串后返回查找的第一个字符位置,找不到返回-1
- replace在替换时,要指定从哪个位置起,多少个字符,替换成什么样的字符串
3.1.6 string字符串比较
功能描述:字符串之间的比较
比较方式:字符串比较是按字符的ASCII码进行对比
- = 返回 0
- > 返回 1
- < 返回 -1
函数原型:
int compare(const string &s) const;与字符串s比较int compare(const char *s) const;与字符串s比较
示例:
xxxxxxxxxx311//字符串比较2void test01()3{4
5 string s1 = "hello";6 string s2 = "aello";7
8 int ret = s1.compare(s2);9
10 if (ret == 0) 11 {12 cout << "s1 等于 s2" << endl;13 }14 else if (ret > 0)15 {16 cout << "s1 大于 s2" << endl;17 }18 else19 {20 cout << "s1 小于 s2" << endl;21 }22
23}24
25int main() 26{27 test01();28
29 system("pause");30 return 0;31}总结:字符串对比主要是用于比较两个字符串是否相等,判断谁大谁小的意义并不是很大。
3.1.7 string字符存取
string中单个字符存取方式有两种:
char& operator[](int n);通过[ ]方式取字符char& at(int n);通过at方法获取字符
示例如下:
xxxxxxxxxx311void test01()2{3 string str = "hello world";4
5 for (int i = 0; i < str.size(); i++)6 {7 cout << str[i] << " ";8 }9 cout << endl;10
11 for (int i = 0; i < str.size(); i++)12 {13 cout << str.at(i) << " ";14 }15 cout << endl;16
17
18 //字符修改19 str[0] = 'x';20 str.at(1) = 'x';21 cout << str << endl;22 23}24
25int main() 26{27 test01();28
29 system("pause");30 return 0;31}总结:string字符串中单个字符存取有两种方式,利用 [ ] 或 at。
3.1.8 string插入和删除
功能描述:对string字符串进行插入和删除字符操作
函数原型:
string& insert(int pos, const char* s);插入字符串string& insert(int pos, const string& str);插入字符串string& insert(int pos, int n, char c);在指定位置插入n个字符cstring& erase(int pos, int n = npos);删除从Pos开始的n个字符
示例如下:
xxxxxxxxxx181//字符串插入和删除2void test01()3{4 string str = "hello";5 str.insert(1, "111");6 cout << str << endl;7
8 str.erase(1, 3); //从1号位置开始3个字符9 cout << str << endl;10}11
12int main() 13{14 test01();15
16 system("pause");17 return 0;18}总结:插入和删除的起始下标都是从0开始。
3.1.9 string子串
功能描述:从字符串中获取想要的子串
函数原型:
string substr(int pos = 0, int n = npos) const;返回由pos开始的n个字符组成的字符串
示例如下:
xxxxxxxxxx221//子串2void test01()3{4
5 string str = "abcdefg";6 string subStr = str.substr(1, 3);7 cout << "subStr = " << subStr << endl;8
9 string email = "hello@sina.com";10 int pos = email.find("@");11 string username = email.substr(0, pos);12 cout << "username: " << username << endl;13
14}15
16int main() 17{18 test01();19
20 system("pause");21 return 0;22}总结:灵活的运用求子串功能,可以在实际开发中获取有效的信息。
3.2 vector容器
3.2.1 vector基本概念
功能:vector数据结构和数组非常相似,也称为单端数组
vector与普通数组区别:不同之处在于数组是静态空间,而vector可以动态扩展
动态扩展:并不是在原空间之后续接新空间,而是找更大的内存空间,然后将原数据拷贝新空间,释放原空间
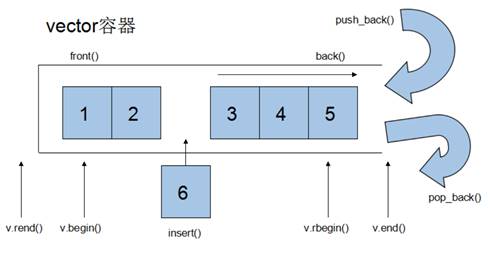
注意:vector容器的迭代器是支持随机访问的迭代器。最常用的就是v.begin()和v.end()。
3.2.2 vector构造函数
功能描述:创建vector容器
函数原型:
vector<T> v;采用模板实现类实现,默认构造函数vector(v.begin(), v.end());将v[begin(), end())区间中的元素拷贝给本身。vector(n, elem);构造函数将n个elem拷贝给本身。vector(const vector &vec);拷贝构造函数。
示例如下:
xxxxxxxxxx371
3void printVector(vector<int>& v) 4{5 for (vector<int>::iterator it = v.begin(); it != v.end(); it++)6 {7 cout << *it << " ";8 }9 cout << endl;10}11
12void test01()13{14 vector<int> v1; //默认构造15 for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++)16 {17 v1.push_back(i);18 }19 printVector(v1);20
21 vector<int> v2(v1.begin(), v1.end()); //v[begin(), end())区间构造22 printVector(v2);23
24 vector<int> v3(10, 100); //n个elem构造25 printVector(v3);26 27 vector<int> v4(v3); //拷贝构造28 printVector(v4);29}30
31int main() 32{33 test01();34
35 system("pause");36 return 0;37}总结:vector的多种构造方式没有可比性,灵活使用即可。
3.2.3 vector赋值操作
功能描述:给vector容器进行赋值
函数原型:
vector& operator=(const vector &vec);重载等号操作符
assign(beg, end);将[beg, end)区间中的数据拷贝赋值给本身。assign(n, elem);将n个elem拷贝赋值给本身。
示例如下:
xxxxxxxxxx411
3void printVector(vector<int>& v) 4{5 for (vector<int>::iterator it = v.begin(); it != v.end(); it++) 6 {7 cout << *it << " ";8 }9 cout << endl;10}11
12//赋值操作13void test01()14{15 vector<int> v1; //无参构造16 for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++)17 {18 v1.push_back(i);19 }20 printVector(v1);21
22 vector<int>v2;23 v2 = v1;24 printVector(v2);25
26 vector<int>v3;27 v3.assign(v1.begin(), v1.end());28 printVector(v3);29
30 vector<int>v4;31 v4.assign(10, 100);32 printVector(v4);33}34
35int main() 36{37 test01();38
39 system("pause");40 return 0;41}总结: vector赋值方式比较简单,使用operator=,或者assign都可以。
3.2.4 vector容量和大小
功能描述:对vector容器的容量和大小操作
函数原型:
empty();判断容器是否为空capacity();容器的容量size();返回容器中元素的个数resize(int num);重新指定容器的长度为num,若容器变长,则以默认值填充新位置。如果容器变短,则末尾超出容器长度的元素被删除。
resize(int num, elem);重新指定容器的长度为num,若容器变长,则以elem值填充新位置。如果容器变短,则末尾超出容器长度的元素被删除
示例如下:
xxxxxxxxxx511
3void printVector(vector<int>& v) 4{5 for (vector<int>::iterator it = v.begin(); it != v.end(); it++) 6 {7 cout << *it << " ";8 }9 cout << endl;10}11
12void test01()13{14 vector<int> v1;15 for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++)16 {17 v1.push_back(i);18 }19 printVector(v1);20 21 if (v1.empty())22 {23 cout << "v1为空" << endl;24 }25 else26 {27 cout << "v1不为空" << endl;28 cout << "v1的容量 = " << v1.capacity() << endl;29 cout << "v1的大小 = " << v1.size() << endl;30 }31
32 //resize 重新指定大小,若指定的更大,默认用0填充新位置,可以利用重载版本替换默认填充33 v1.resize(15,10);34 printVector(v1);35 cout << "v1的容量 = " << v1.capacity() << endl; //1936 cout << "v1的大小 = " << v1.size() << endl; //1537
38 //resize 重新指定大小,若指定的更小,超出部分元素被删除39 v1.resize(5);40 printVector(v1);41 cout << "v1的容量 = " << v1.capacity() << endl; //1942 cout << "v1的大小 = " << v1.size() << endl; //543}44
45int main()46{47 test01();48
49 system("pause");50 return 0;51}3.2.5 vector插入和删除
功能描述:对vector容器进行插入、删除操作
函数原型:
push_back(ele);尾部插入元素elepop_back();删除最后一个元素insert(const_iterator pos, ele);迭代器指向位置pos插入元素eleinsert(const_iterator pos, int count,ele);迭代器指向位置pos插入count个元素eleerase(const_iterator pos);删除迭代器指向的元素erase(const_iterator start, const_iterator end);删除迭代器从start到end之间的元素clear();删除容器中所有元素
示例如下:
xxxxxxxxxx491
3void printVector(vector<int>& v) 4{5 for (vector<int>::iterator it = v.begin(); it != v.end(); it++) 6 {7 cout << *it << " ";8 }9 cout << endl;10}11
12//插入和删除13void test01()14{15 vector<int> v1;16 //尾插17 v1.push_back(10);18 v1.push_back(20);19 v1.push_back(30);20 v1.push_back(40);21 v1.push_back(50);22 printVector(v1);23 //尾删24 v1.pop_back();25 printVector(v1);26 //插入27 v1.insert(v1.begin(), 100);28 printVector(v1);29
30 v1.insert(v1.begin(), 2, 1000);31 printVector(v1);32
33 //删除34 v1.erase(v1.begin());35 printVector(v1);36
37 //清空38 v1.erase(v1.begin(), v1.end());39 v1.clear();40 printVector(v1);41}42
43int main() 44{45 test01();46
47 system("pause");48 return 0;49}3.2.6 vector数据存取
功能描述:对vector中的数据的存取操作
函数原型:
at(int idx);返回索引idx所指的数据operator[];返回索引idx所指的数据front();返回容器中第一个数据元素back();返回容器中最后一个数据元素
示例如下:
xxxxxxxxxx331
3void test01()4{5 vector<int>v1;6 for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++)7 {8 v1.push_back(i);9 }10
11 for (int i = 0; i < v1.size(); i++)12 {13 cout << v1[i] << " ";14 }15 cout << endl;16
17 for (int i = 0; i < v1.size(); i++)18 {19 cout << v1.at(i) << " ";20 }21 cout << endl;22
23 cout << "v1的第一个元素为: " << v1.front() << endl;24 cout << "v1的最后一个元素为: " << v1.back() << endl;25}26
27int main()28{29 test01();30
31 system("pause");32 return 0;33}总结:
- 除了用迭代器获取vector容器中元素,[ ]和at也可以
- front返回容器第一个元素
- back返回容器最后一个元素
3.2.7 vector互换容器
功能描述:实现两个容器内元素进行互换
函数原型:swap(vec); 将vec与本身的元素互换
示例如下:
xxxxxxxxxx671
3void printVector(vector<int>& v) 4{5 for (vector<int>::iterator it = v.begin(); it != v.end(); it++) 6 {7 cout << *it << " ";8 }9 cout << endl;10}11
12void test01()13{14 vector<int>v1;15 for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++)16 {17 v1.push_back(i);18 }19 printVector(v1);20
21 vector<int>v2;22 for (int i = 10; i > 0; i--)23 {24 v2.push_back(i);25 }26 printVector(v2);27
28 //互换容器29 cout << "互换后" << endl;30 v1.swap(v2);31 printVector(v1);32 printVector(v2);33}34
35void test02()36{37 vector<int> v;38 for (int i = 0; i < 100000; i++) 39 {40 v.push_back(i);41 }42
43 cout << "v的容量为:" << v.capacity() << endl; //130000多44 cout << "v的大小为:" << v.size() << endl; //10000045
46 v.resize(3);47
48 cout << "v的容量为:" << v.capacity() << endl; //130000多49 cout << "v的大小为:" << v.size() << endl; //3内存浪费严重50
51 //收缩内存52 vector<int>(v).swap(v);53 //匿名对象拷贝构造,拷贝构造会根据v的size进行,容量变小,然后容器互换,匿名对象执行完这行代码被系统回收54 55 cout << "v的容量为:" << v.capacity() << endl; //356 cout << "v的大小为:" << v.size() << endl; //357}58
59int main() 60{61 test01();62
63 test02();64
65 system("pause");66 return 0;67}总结:swap可以使两个容器互换,可以达到实用的收缩内存效果。
3.2.8 vector预留空间
功能描述:减少vector在动态扩展容量时的扩展次数
函数原型:reserve(int len); 容器预留len个元素长度,预留位置不初始化,元素不可访问。
示例如下:
xxxxxxxxxx321
3void test01()4{5 vector<int> v;6
7 //预留空间,没有预留空间的话会扩展30次内存8 v.reserve(100000);9
10 int num = 0;11 int* p = NULL;12 for (int i = 0; i < 100000; i++) 13 {14 v.push_back(i);15 16 if (p != &v[0]) 17 {18 p = &v[0];19 num++;20 }21 }22
23 cout << "num:" << num << endl;24}25
26int main() 27{28 test01();29 30 system("pause");31 return 0;32}总结:如果数据量较大,可以一开始利用reserve预留空间,减少vector在动态扩展容量时的扩展次数。
3.3 deque容器
3.3.1 deque容器基本概念
功能:双端数组,可以对头端进行插入删除操作
deque与vector区别:
- vector对于头部的插入删除效率低,数据量越大,效率越低
- deque相对而言,对头部的插入删除速度会比vector快
- vector访问元素时的速度会比deque快,这和两者内部实现有关
deque内部工作原理:
deque内部有个中控器,维护每段缓冲区中的内容,缓冲区中存放真实数据
中控器维护的是每个缓冲区的地址,使得使用deque时像一片连续的内存空间
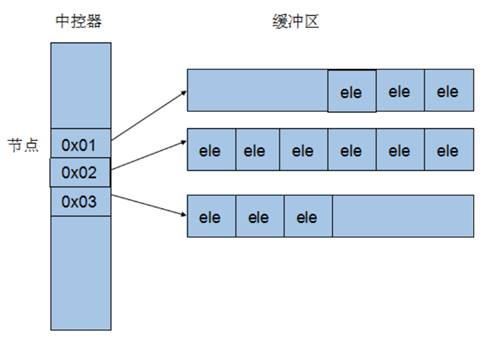
注意:deque容器的迭代器也是支持随机访问的。
3.3.2 deque构造函数
功能描述:deque容器构造
函数原型:
deque<T> deqT;默认构造形式deque(beg, end);构造函数将[beg, end)区间中的元素拷贝给本身。deque(n, elem);构造函数将n个elem拷贝给本身。deque(const deque &deq);拷贝构造函数
示例如下:
xxxxxxxxxx401
3void printDeque(const deque<int>& d) 4{5 for (deque<int>::const_iterator it = d.begin(); it != d.end(); it++) 6 {7 cout << *it << " ";8
9 }10 cout << endl;11}12
13//deque构造14void test01() 15{16 deque<int> d1; //无参构造函数17 for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++)18 {19 d1.push_back(i);20 }21 printDeque(d1);22 23 deque<int> d2(d1.begin(),d1.end());24 printDeque(d2);25
26 deque<int>d3(10,100);27 printDeque(d3);28
29 deque<int>d4 = d3;30 printDeque(d4);31}32
33int main() 34{35 test01();36
37 system("pause");38
39 return 0;40}总结:deque容器和vector容器的构造方式几乎一致,灵活使用即可。
3.3.3 deque赋值操作
功能描述:给deque容器进行赋值
函数原型:
deque& operator=(const deque &deq);重载等号操作符
assign(beg, end);将[beg, end)区间中的数据拷贝赋值给本身。assign(n, elem);将n个elem拷贝赋值给本身。
示例如下:
xxxxxxxxxx441
3void printDeque(const deque<int>& d) 4{5 for (deque<int>::const_iterator it = d.begin(); it != d.end(); it++) 6 {7 cout << *it << " ";8
9 }10 cout << endl;11}12
13//赋值操作14void test01()15{16 deque<int> d1;17 for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++)18 {19 d1.push_back(i);20 }21 printDeque(d1);22
23 deque<int>d2;24 d2 = d1;25 printDeque(d2);26
27 deque<int>d3;28 d3.assign(d1.begin(), d1.end());29 printDeque(d3);30
31 deque<int>d4;32 d4.assign(10, 100);33 printDeque(d4);34
35}36
37int main() 38{39 test01();40
41 system("pause");42
43 return 0;44}总结:deque赋值操作也与vector相同,需熟练掌握。
3.3.4 deque大小操作
功能描述:对deque容器的大小进行操作
函数原型:
deque.empty();判断容器是否为空deque.size();返回容器中元素的个数deque.resize(num);重新指定容器的长度为num,若容器变长,则以默认值填充新位置。如果容器变短,则末尾超出容器长度的元素被删除。
deque.resize(num, elem);重新指定容器的长度为num,若容器变长,则以elem值填充新位置。如果容器变短,则末尾超出容器长度的元素被删除。
示例如下:
xxxxxxxxxx501
3void printDeque(const deque<int>& d) 4{5 for (deque<int>::const_iterator it = d.begin(); it != d.end(); it++) 6 {7 cout << *it << " ";8
9 }10 cout << endl;11}12
13//大小操作14void test01()15{16 deque<int> d1;17 for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++)18 {19 d1.push_back(i);20 }21 printDeque(d1);22
23 //判断容器是否为空24 if (d1.empty()) 25 {26 cout << "d1为空!" << endl;27 }28 else 29 {30 cout << "d1不为空!" << endl;31 //统计大小32 cout << "d1的大小为:" << d1.size() << endl;33 }34
35 //重新指定大小36 d1.resize(15, 1);37 printDeque(d1);38
39 d1.resize(5);40 printDeque(d1);41}42
43int main() 44{45 test01();46
47 system("pause");48
49 return 0;50}注意:deque没有容量的概念。
3.3.5 deque 插入和删除
功能描述:向deque容器中插入和删除数据
函数原型:
两端插入操作:
push_back(elem);在容器尾部添加一个数据push_front(elem);在容器头部插入一个数据pop_back();删除容器最后一个数据pop_front();删除容器第一个数据
指定位置操作:
insert(pos,elem);在pos位置插入一个elem元素的拷贝,返回新数据的位置。insert(pos,n,elem);在pos位置插入n个elem数据,无返回值。insert(pos,beg,end);在pos位置插入[beg,end)区间的数据,无返回值。clear();清空容器的所有数据erase(beg,end);删除[beg,end)区间的数据,返回下一个数据的位置。erase(pos);删除pos位置的数据,返回下一个数据的位置。
示例如下:
xxxxxxxxxx881
3void printDeque(const deque<int>& d) 4{5 for (deque<int>::const_iterator it = d.begin(); it != d.end(); it++) 6 {7 cout << *it << " ";8
9 }10 cout << endl;11}12
13//两端插入操作14void test01()15{16 deque<int> d;17 //尾插18 d.push_back(10);19 d.push_back(20);20 //头插21 d.push_front(100);22 d.push_front(200);23
24 printDeque(d);25
26 //尾删27 d.pop_back();28 //头删29 d.pop_front();30 printDeque(d);31}32
33//指定位置插入操作34void test02()35{36 deque<int> d;37 d.push_back(10);38 d.push_back(20);39 d.push_front(100);40 d.push_front(200);41 printDeque(d);42
43 d.insert(d.begin(), 1000);44 printDeque(d);45
46 d.insert(d.begin(), 2,10000);47 printDeque(d);48
49 deque<int>d2;50 d2.push_back(1);51 d2.push_back(2);52 d2.push_back(3);53
54 d.insert(d.begin(), d2.begin(), d2.end());55 printDeque(d);56
57}58
59//删除60void test03()61{62 deque<int> d;63 d.push_back(10);64 d.push_back(20);65 d.push_front(100);66 d.push_front(200);67 printDeque(d);68
69 d.erase(d.begin());70 printDeque(d);71
72 d.erase(d.begin(), d.end());73 d.clear();74 printDeque(d);75}76
77int main() 78{79 test01();80
81 test02();82
83 test03();84 85 system("pause");86
87 return 0;88}注意:插入和删除提供的位置是迭代器!
3.3.6 deque 数据存取
功能描述:对deque 中的数据的存取操作
函数原型:
at(int idx);返回索引idx所指的数据operator[];返回索引idx所指的数据front();返回容器中第一个数据元素back();返回容器中最后一个数据元素
示例如下:
xxxxxxxxxx491
3void printDeque(const deque<int>& d) 4{5 for (deque<int>::const_iterator it = d.begin(); it != d.end(); it++) 6 {7 cout << *it << " ";8
9 }10 cout << endl;11}12
13//数据存取14void test01()15{16
17 deque<int> d;18 d.push_back(10);19 d.push_back(20);20 d.push_front(100);21 d.push_front(200);22
23 for (int i = 0; i < d.size(); i++) 24 {25 cout << d[i] << " ";26 }27 cout << endl;28
29
30 for (int i = 0; i < d.size(); i++) 31 {32 cout << d.at(i) << " ";33 }34 cout << endl;35
36 cout << "front:" << d.front() << endl;37
38 cout << "back:" << d.back() << endl;39
40}41
42int main() 43{44 test01();45
46 system("pause");47
48 return 0;49}总结:
- 除了用迭代器获取deque容器中元素,[ ]和at也可以
- front返回容器第一个元素
- back返回容器最后一个元素
3.3.7 deque 排序
功能描述:利用算法实现对deque容器进行排序
算法:sort(iterator beg, iterator end) 对beg和end区间内元素进行排序
示例如下:
xxxxxxxxxx361//标准算法头文件3
4void printDeque(const deque<int>& d) 5{6 for (deque<int>::const_iterator it = d.begin(); it != d.end(); it++) 7 {8 cout << *it << " ";9
10 }11 cout << endl;12}13
14void test01()15{16
17 deque<int> d;18 d.push_back(10);19 d.push_back(20);20 d.push_front(100);21 d.push_front(200);22
23 printDeque(d);24 sort(d.begin(), d.end());25 printDeque(d);26
27}28
29int main() 30{31 test01();32
33 system("pause");34
35 return 0;36}总结:sort算法非常实用,使用时包含头文件 algorithm即可。对于支持随机访问的迭代器的容器,都可以直接利用sort()算法进行排序,比如:vector容器也可以利用sort()进行排序。
3.4 案例-评委打分
3.4.1 案例描述
有5名选手:选手ABCDE,10个评委分别对每一名选手打分,去除最高分,去除最低分,取平均分。
3.4.2 实现步骤
- 创建五名选手,放到vector中
- 遍历vector容器,取出来每一个选手,执行for循环,可以把10个评分打分存到deque容器中
- sort算法对deque容器中分数排序,去除最高和最低分
- deque容器遍历一遍,累加总分
- 获取平均分
示例代码:
xxxxxxxxxx1061//选手类2class Person3{4public:5 Person(string name, int score)6 {7 this->m_Name = name;8 this->m_Score = score;9 }10
11 string m_Name; //姓名12 int m_Score; //平均分13};14
15void createPerson(vector<Person>&v)16{17 string nameSeed = "ABCDE";18 for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++)19 {20 string name = "选手";21 name += nameSeed[i];22
23 int score = 0;24
25 Person p(name, score);26
27 //将创建的person对象放入到容器中28 v.push_back(p);29 }30}31
32//打分33void setScore(vector<Person>&v)34{35 for (vector<Person>::iterator it = v.begin(); it != v.end(); it++)36 {37 //将评委的分数 放入到deque容器中38 deque<int>d;39 for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++)40 {41 int score = rand() % 41 + 60; // 60 ~ 10042 d.push_back(score);43 }44
45 //cout << "选手: " << it->m_Name << " 打分: " << endl;46 //for (deque<int>::iterator dit = d.begin(); dit != d.end(); dit++)47 //{48 // cout << *dit << " ";49 //}50 //cout << endl;51
52 //排序53 sort(d.begin(), d.end());54
55 //去除最高和最低分56 d.pop_back();57 d.pop_front();58
59 //取平均分60 int sum = 0;61 for (deque<int>::iterator dit = d.begin(); dit != d.end(); dit++)62 {63 sum += *dit; //累加每个评委的分数64 }65
66 int avg = sum / d.size();67
68 //将平均分 赋值给选手身上69 it->m_Score = avg;70 }71
72}73
74void showScore(vector<Person>&v)75{76 for (vector<Person>::iterator it = v.begin(); it != v.end(); it++)77 {78 cout << "姓名: " << it->m_Name << " 平均分: " << it->m_Score << endl;79 }80}81
82int main() 83{84 //随机数种子85 srand((unsigned int)time(NULL));86
87 //1.创建5名选手88 vector<Person>v; //存放选手容器89 createPerson(v);90
91 //测试92 //for (vector<Person>::iterator it = v.begin(); it != v.end(); it++)93 //{94 // cout << "姓名: " << (*it).m_Name << " 分数: " << (*it).m_Score << endl;95 //}96
97 //2.给5名选手打分98 setScore(v);99
100 //3.显示最后得分101 showScore(v);102
103 system("pause");104
105 return 0;106}总结: 选取不同的容器操作数据,可以提升代码的效率。
3.5 stack容器
3.5.1 stack 基本概念
概念:stack是一种先进后出(First In Last Out,FILO)的数据结构,它只有一个出口。
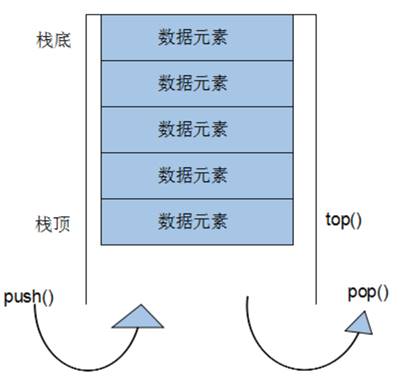
栈中只有顶端的元素才可以被外界使用,因此栈不允许有遍历行为。
栈中进入数据称为:入栈 push
栈中弹出数据称为:出栈 pop
3.5.2 stack 常用接口
功能描述:栈容器常用的对外接口
构造函数:
stack<T> stk;stack采用模板类实现, stack对象的默认构造形式stack(const stack &stk);拷贝构造函数
赋值操作:
stack& operator=(const stack &stk);重载等号操作符
数据存取:
push(elem);向栈顶添加元素pop();从栈顶移除第一个元素top();返回栈顶元素
大小操作:
empty();判断堆栈是否为空size();返回栈的大小
示例如下:
xxxxxxxxxx331
3//栈容器常用接口4void test01()5{6 //创建栈容器 栈容器必须符合先进后出7 stack<int> s;8
9 //向栈中添加元素,叫做压栈或入栈10 s.push(10);11 s.push(20);12 s.push(30);13
14 cout << "栈的大小为:" << s.size() << endl;15 while (!s.empty()) 16 {17 //输出栈顶元素18 cout << "栈顶元素为: " << s.top() << endl;19 //弹出栈顶元素20 s.pop();21 }22 cout << "栈的大小为:" << s.size() << endl;23
24}25
26int main() 27{28 test01();29
30 system("pause");31
32 return 0;33}3.6 queue 容器
3.6.1 queue 基本概念
概念:Queue是一种先进先出(First In First Out,FIFO)的数据结构,它有两个出口。
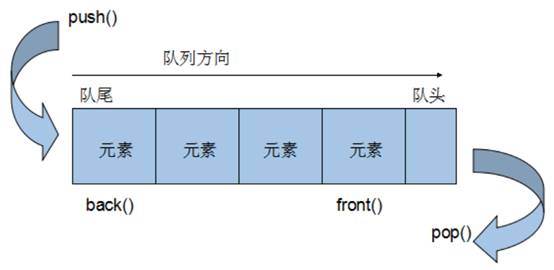
队列容器允许从一端新增元素,从另一端移除元素
队列中只有队头和队尾才可以被外界使用,因此队列不允许有遍历行为
队列中进数据称为:入队 push
队列中出数据称为:出队 pop
3.6.2 queue 常用接口
功能描述:栈容器常用的对外接口
构造函数:
queue<T> que;queue采用模板类实现,queue对象的默认构造形式queue(const queue &que);拷贝构造函数
赋值操作:
queue& operator=(const queue &que);重载等号操作符
数据存取:
push(elem);往队尾添加元素pop();从队头移除第一个元素back();返回最后一个元素front();返回第一个元素
大小操作:
empty();判断堆栈是否为空size();返回栈的大小
示例如下:
xxxxxxxxxx601
4class Person5{6public:7 Person(string name, int age)8 {9 this->m_Name = name;10 this->m_Age = age;11 }12
13 string m_Name;14 int m_Age;15};16
17void test01() 18{19 //创建队列20 queue<Person> q;21
22 //准备数据23 Person p1("唐僧", 30);24 Person p2("孙悟空", 1000);25 Person p3("猪八戒", 900);26 Person p4("沙僧", 800);27
28 //向队列中添加元素,入队操作29 q.push(p1);30 q.push(p2);31 q.push(p3);32 q.push(p4);33
34 cout << "队列大小为:" << q.size() << endl;35 //队列不提供迭代器,更不支持随机访问 36 while (!q.empty()) 37 {38 //输出队头元素39 cout << "队头元素-- 姓名: " << q.front().m_Name 40 << " 年龄: "<< q.front().m_Age << endl;41 42 cout << "队尾元素-- 姓名: " << q.back().m_Name 43 << " 年龄: " << q.back().m_Age << endl;44 45 cout << endl;46 //弹出队头元素47 q.pop();48 }49
50 cout << "队列大小为:" << q.size() << endl;51}52
53int main() 54{55 test01();56
57 system("pause");58
59 return 0;60}3.7 list容器
3.7.1 list基本概念
功能:将数据进行链式存储
链表(list)是一种物理存储单元上非连续的存储结构,数据元素的逻辑顺序是通过链表中的指针链接实现的
链表的组成:链表由一系列结点组成
结点的组成:一个是存储数据元素的数据域,另一个是存储下一个结点地址的指针域
STL中的链表是一个双向循环链表:双向是指针域有两个指针,一个指向前一个节点,一个指向后一个节点。循环是第一个节点的头指针指向最后一个节点,最后一个节点的尾指针指向第一个节点。
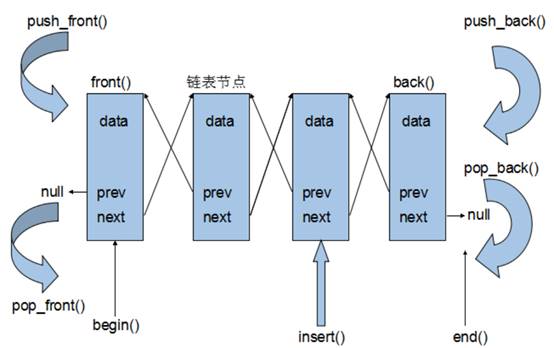
由于链表的存储方式并不是连续的内存空间,因此链表list中的迭代器只支持前移和后移,属于双向迭代器
list的优点:
- 采用动态存储分配,不会造成内存浪费和溢出
- 链表执行插入和删除操作十分方便,修改指针即可,不需要移动大量元素
- List有一个重要的性质,插入操作和删除操作都不会造成原有list迭代器的失效,这在vector是不成立的。
list的缺点:
- 链表灵活,但是空间(指针域)和 时间(遍历)额外耗费较大
总结:STL中List和vector是两个最常被使用的容器,各有优缺点,要根据需求合理选择。
3.7.2 list构造函数
功能描述:创建list容器
函数原型:
list<T> lst;list采用采用模板类实现,对象的默认构造形式:list(beg,end);构造函数将[beg, end)区间中的元素拷贝给本身。list(n,elem);构造函数将n个elem拷贝给本身。list(const list &lst);拷贝构造函数。
示例如下:
xxxxxxxxxx391
3void printList(const list<int>& L) 4{5 for (list<int>::const_iterator it = L.begin(); it != L.end(); it++) 6 {7 cout << *it << " ";8 }9 cout << endl;10}11
12void test01()13{14 list<int>L1;15 L1.push_back(10);16 L1.push_back(20);17 L1.push_back(30);18 L1.push_back(40);19
20 printList(L1);21
22 list<int>L2(L1.begin(),L1.end());23 printList(L2);24
25 list<int>L3(L2);26 printList(L3);27
28 list<int>L4(10, 1000);29 printList(L4);30}31
32int main() 33{34 test01();35
36 system("pause");37
38 return 0;39}总结:list的构造方式类似于其他几个STL常用容器。
3.7.3 list 赋值和交换
功能描述:给list容器进行赋值,以及交换list容器
函数原型:
assign(beg, end);将[beg, end)区间中的数据拷贝赋值给本身。assign(n, elem);将n个elem拷贝赋值给本身。list& operator=(const list &lst);重载等号操作符swap(lst);将lst与本身的元素互换。
示例如下:
xxxxxxxxxx711
3void printList(const list<int>& L) 4{5 for (list<int>::const_iterator it = L.begin(); it != L.end(); it++) 6 {7 cout << *it << " ";8 }9 cout << endl;10}11
12//赋值和交换13void test01()14{15 list<int>L1;16 L1.push_back(10);17 L1.push_back(20);18 L1.push_back(30);19 L1.push_back(40);20 printList(L1);21
22 //赋值23 list<int>L2;24 L2 = L1;25 printList(L2);26
27 list<int>L3;28 L3.assign(L2.begin(), L2.end());29 printList(L3);30
31 list<int>L4;32 L4.assign(10, 100);33 printList(L4);34
35}36
37//交换38void test02()39{40
41 list<int>L1;42 L1.push_back(10);43 L1.push_back(20);44 L1.push_back(30);45 L1.push_back(40);46
47 list<int>L2;48 L2.assign(10, 100);49
50 cout << "交换前: " << endl;51 printList(L1);52 printList(L2);53 cout << endl;54
55 L1.swap(L2);56 cout << "交换后: " << endl;57 printList(L1);58 printList(L2);59
60}61
62int main() 63{64 test01();65
66 test02();67
68 system("pause");69
70 return 0;71}3.7.4 list 大小操作
功能描述:对list容器的大小进行操作
函数原型:
size();返回容器中元素的个数empty();判断容器是否为空resize(num);重新指定容器的长度为num,若容器变长,则以默认值填充新位置。如果容器变短,则末尾超出容器长度的元素被删除。
resize(num, elem);重新指定容器的长度为num,若容器变长,则以elem值填充新位置。如果容器变短,则末尾超出容器长度的元素被删除。
示例如下:
xxxxxxxxxx461
3void printList(const list<int>& L) 4{5 for (list<int>::const_iterator it = L.begin(); it != L.end(); it++) 6 {7 cout << *it << " ";8 }9 cout << endl;10}11
12//大小操作13void test01()14{15 list<int>L1;16 L1.push_back(10);17 L1.push_back(20);18 L1.push_back(30);19 L1.push_back(40);20
21 if (L1.empty())22 {23 cout << "L1为空" << endl;24 }25 else26 {27 cout << "L1不为空" << endl;28 cout << "L1的大小为: " << L1.size() << endl;29 }30
31 //重新指定大小32 L1.resize(10);33 printList(L1);34
35 L1.resize(2);36 printList(L1);37}38
39int main() 40{41 test01();42
43 system("pause");44
45 return 0;46}3.7.5 list 插入和删除
功能描述:对list容器进行数据的插入和删除
函数原型:
push_back(elem);在容器尾部加入一个元素pop_back();删除容器中最后一个元素push_front(elem);在容器开头插入一个元素pop_front();从容器开头移除第一个元素insert(pos,elem);在pos位置插elem元素的拷贝,返回新数据的位置。insert(pos,n,elem);在pos位置插入n个elem数据,无返回值。insert(pos,beg,end);在pos位置插入[beg,end)区间的数据,无返回值。clear();移除容器的所有数据erase(beg,end);删除[beg,end)区间的数据,返回下一个数据的位置。erase(pos);删除pos位置的数据,返回下一个数据的位置。remove(elem);删除容器中所有与elem值匹配的元素。
示例如下:
xxxxxxxxxx651
3void printList(const list<int>& L) 4{5 for (list<int>::const_iterator it = L.begin(); it != L.end(); it++) 6 {7 cout << *it << " ";8 }9 cout << endl;10}11
12//插入和删除13void test01()14{15 list<int> L;16 //尾插17 L.push_back(10);18 L.push_back(20);19 L.push_back(30);20 //头插21 L.push_front(100);22 L.push_front(200);23 L.push_front(300);24
25 printList(L);26
27 //尾删28 L.pop_back();29 printList(L);30
31 //头删32 L.pop_front();33 printList(L);34
35 //插入36 list<int>::iterator it = L.begin();37 L.insert(++it, 1000);38 printList(L);39
40 //删除41 it = L.begin();42 L.erase(++it);43 printList(L);44
45 //移除46 L.push_back(10000);47 L.push_back(10000);48 L.push_back(10000);49 printList(L);50 L.remove(10000);51 printList(L);52 53 //清空54 L.clear();55 printList(L);56}57
58int main()59{60 test01();61
62 system("pause");63
64 return 0;65}3.7.6 list 数据存取
功能描述:对list容器中数据进行存取
函数原型:
front();返回第一个元素。back();返回最后一个元素。
示例如下:
xxxxxxxxxx301
3//数据存取4void test01()5{6 list<int>L1;7 L1.push_back(10);8 L1.push_back(20);9 L1.push_back(30);10 L1.push_back(40);11
12 13 //cout << L1.at(0) << endl; //错误 不支持at访问数据14 //cout << L1[0] << endl; //错误 不支持[]方式访问数据15 cout << "第一个元素为: " << L1.front() << endl;16 cout << "最后一个元素为: " << L1.back() << endl;17
18 //list容器的迭代器是双向迭代器,不支持随机访问19 list<int>::iterator it = L1.begin();20 //it = it + 1;//错误,不可以跳跃访问,即使是+121}22
23int main() 24{25 test01();26
27 system("pause");28
29 return 0;30}注意:list容器中不可以通过[ ]或者at方式访问数据。
3.7.7 list 反转和排序
功能描述:将容器中的元素反转,以及将容器中的数据进行排序
函数原型:
reverse();反转链表sort();链表排序
示例如下:
xxxxxxxxxx471void printList(const list<int>& L) 2{3 for (list<int>::const_iterator it = L.begin(); it != L.end(); it++) 4 {5 cout << *it << " ";6 }7 cout << endl;8}9
10bool myCompare(int val1 , int val2)11{12 return val1 > val2;13}14
15//反转和排序16void test01()17{18 list<int> L;19 L.push_back(90);20 L.push_back(30);21 L.push_back(20);22 L.push_back(70);23 printList(L);24
25 //反转容器的元素26 L.reverse();27 printList(L);28
29 //排序30 //所有不支持随机访问迭代器的容器,不可以用标准算法31 //不支持随机访问迭代器的容器,内部会提供对应的一些算法32 //sort(L.begin(),L.end()),错误!33 L.sort(); //默认的排序规则 从小到大34 printList(L);35
36 L.sort(myCompare); //指定规则,从大到小37 printList(L);38}39
40int main() 41{42 test01();43
44 system("pause");45
46 return 0;47}注意:对于不支持随机访问迭代器的容器,要使用成员函数来进行排序。
3.7.8 排序案例
案例描述:将Person自定义数据类型进行排序,Person中属性有姓名、年龄、身高
排序规则:按照年龄进行升序,如果年龄相同按照身高进行降序
示例如下:
xxxxxxxxxx751
4class Person 5{6public:7 Person(string name, int age , int height) 8 {9 m_Name = name;10 m_Age = age;11 m_Height = height;12 }13
14public:15 string m_Name; //姓名16 int m_Age; //年龄17 int m_Height; //身高18};19
20
21bool ComparePerson(Person& p1, Person& p2) 22{23 if (p1.m_Age == p2.m_Age) 24 {25 return p1.m_Height > p2.m_Height;26 }27 else28 {29 return p1.m_Age < p2.m_Age;30 }31
32}33
34void test01() 35{36 list<Person> L;37
38 Person p1("刘备", 35 , 175);39 Person p2("曹操", 45 , 180);40 Person p3("孙权", 40 , 170);41 Person p4("赵云", 25 , 190);42 Person p5("张飞", 35 , 160);43 Person p6("关羽", 35 , 200);44
45 L.push_back(p1);46 L.push_back(p2);47 L.push_back(p3);48 L.push_back(p4);49 L.push_back(p5);50 L.push_back(p6);51
52 for (list<Person>::iterator it = L.begin(); it != L.end(); it++) 53 {54 cout << "姓名: " << it->m_Name << " 年龄: " << it->m_Age 55 << " 身高: " << it->m_Height << endl;56 }57
58 cout << "--------------------------------------" << endl;59 L.sort(ComparePerson); //高级排序60
61 for (list<Person>::iterator it = L.begin(); it != L.end(); it++) 62 {63 cout << "姓名: " << it->m_Name << " 年龄: " << it->m_Age 64 << " 身高: " << it->m_Height << endl;65 }66}67
68int main() 69{70 test01();71
72 system("pause");73
74 return 0;75}总结:
- 对于自定义数据类型,必须要指定排序规则,否则编译器不知道如何进行排序
- 高级排序只是在排序规则上再进行一次逻辑规则制定,并不复杂
3.8 set/multiset 容器
3.8.1 set基本概念
特点:所有元素都会在插入时自动被排序
本质:set/multiset属于关联式容器,底层结构是用二叉树实现。
set和multiset区别:
- set不允许容器中有重复的元素
- multiset允许容器中有重复的元素
3.8.2 set构造和赋值
功能描述:创建set容器以及赋值
构造:
set<T> st;默认构造函数:set(const set &st);拷贝构造函数
赋值:
set& operator=(const set &st);重载等号操作符
示例如下:
xxxxxxxxxx411
3void printSet(set<int> & s)4{5 for (set<int>::iterator it = s.begin(); it != s.end(); it++)6 {7 cout << *it << " ";8 }9 cout << endl;10}11
12//构造和赋值13void test01()14{15 set<int> s1;16
17 s1.insert(10);18 s1.insert(30);19 s1.insert(20);20 s1.insert(40);21 s1.insert(30); //重复不会报错,也插不进去22 printSet(s1);23
24 //拷贝构造25 set<int>s2(s1);26 printSet(s2);27
28 //赋值29 set<int>s3;30 s3 = s2;31 printSet(s3);32}33
34int main() 35{36 test01();37
38 system("pause");39
40 return 0;41}总结:
- set容器插入数据时用insert
- set容器插入数据的数据会自动排序
3.8.3 set大小和交换
功能描述:统计set容器大小以及交换set容器
函数原型:
size();返回容器中元素的数目empty();判断容器是否为空swap(st);交换两个集合容器
示例如下:
xxxxxxxxxx721
3void printSet(set<int> & s)4{5 for (set<int>::iterator it = s.begin(); it != s.end(); it++)6 {7 cout << *it << " ";8 }9 cout << endl;10}11
12//大小13void test01()14{15
16 set<int> s1;17 18 s1.insert(10);19 s1.insert(30);20 s1.insert(20);21 s1.insert(40);22
23 if (s1.empty())24 {25 cout << "s1为空" << endl;26 }27 else28 {29 cout << "s1不为空" << endl;30 cout << "s1的大小为: " << s1.size() << endl;31 }32
33}34
35//交换36void test02()37{38 set<int> s1;39
40 s1.insert(10);41 s1.insert(30);42 s1.insert(20);43 s1.insert(40);44
45 set<int> s2;46
47 s2.insert(100);48 s2.insert(300);49 s2.insert(200);50 s2.insert(400);51
52 cout << "交换前" << endl;53 printSet(s1);54 printSet(s2);55 cout << endl;56
57 cout << "交换后" << endl;58 s1.swap(s2);59 printSet(s1);60 printSet(s2);61}62
63int main() 64{65 test01();66
67 test02();68
69 system("pause");70
71 return 0;72}3.8.4 set插入和删除
功能描述:set容器进行插入数据和删除数据
函数原型:
insert(elem);在容器中插入元素。clear();清除所有元素erase(pos);删除pos迭代器所指的元素,返回下一个元素的迭代器。erase(beg, end);删除区间[beg,end)的所有元素 ,返回下一个元素的迭代器。erase(elem);删除容器中值为elem的元素。
示例如下:
xxxxxxxxxx431
3void printSet(set<int> & s)4{5 for (set<int>::iterator it = s.begin(); it != s.end(); it++)6 {7 cout << *it << " ";8 }9 cout << endl;10}11
12//插入和删除13void test01()14{15 set<int> s1;16 //插入17 s1.insert(10);18 s1.insert(30);19 s1.insert(20);20 s1.insert(40);21 printSet(s1);22
23 //删除24 s1.erase(s1.begin());25 printSet(s1);26
27 s1.erase(30);28 printSet(s1);29
30 //清空31 //s1.erase(s1.begin(), s1.end());32 s1.clear();33 printSet(s1);34}35
36int main() 37{38 test01();39
40 system("pause");41
42 return 0;43}3.8.5 set查找和统计
功能描述:对set容器进行查找数据以及统计数据
函数原型:
find(key);查找key是否存在,若存在,返回该键的元素的迭代器;若不存在,返回set.end();count(key);统计key的元素个数
示例如下:
xxxxxxxxxx371
3//查找和统计4void test01()5{6 set<int> s1;7 //插入8 s1.insert(10);9 s1.insert(30);10 s1.insert(20);11 s1.insert(40);12 13 //查找14 set<int>::iterator pos = s1.find(30);15
16 if (pos != s1.end())17 {18 cout << "找到了元素 : " << *pos << endl;19 }20 else21 {22 cout << "未找到元素" << endl;23 }24
25 //统计26 int num = s1.count(30);27 cout << "num = " << num << endl;28}29
30int main() 31{32 test01();33
34 system("pause");35
36 return 0;37}总结:
- 查找返回的是迭代器
- 统计对于set,结果为0或者1
3.8.6 set和multiset区别
区别:
- set不可以插入重复数据,而multiset可以
- set插入数据的同时会返回插入结果,表示插入是否成功
- multiset不会检测数据,因此可以插入重复数据
示例如下:
xxxxxxxxxx421
3//set和multiset区别4void test01()5{6 set<int> s;7 pair<set<int>::iterator, bool> ret = s.insert(10);8 if (ret.second) {9 cout << "第一次插入成功!" << endl;10 }11 else {12 cout << "第一次插入失败!" << endl;13 }14
15 ret = s.insert(10);16 if (ret.second) {17 cout << "第二次插入成功!" << endl;18 }19 else {20 cout << "第二次插入失败!" << endl;21 }22 23 //multiset24 multiset<int> ms;25 ms.insert(10);26 ms.insert(10);27
28 for (multiset<int>::iterator it = ms.begin(); it != ms.end(); it++) 29 {30 cout << *it << " ";31 }32 cout << endl;33}34
35int main() 36{37 test01();38
39 system("pause");40
41 return 0;42}总结:
- 如果不允许插入重复数据可以利用set
- 如果需要插入重复数据则利用multiset
3.8.7 pair对组创建
功能描述:成对出现的数据,利用对组可以返回两个数据
两种创建方式:
pair<type, type> p ( value1, value2 );pair<type, type> p = make_pair( value1, value2 );
示例如下:
xxxxxxxxxx201
3//对组创建4void test01()5{6 pair<string, int> p(string("Tom"), 20);7 cout << "姓名: " << p.first << " 年龄: " << p.second << endl;8
9 pair<string, int> p2 = make_pair("Jerry", 10);10 cout << "姓名: " << p2.first << " 年龄: " << p2.second << endl;11}12
13int main() 14{15 test01();16
17 system("pause");18
19 return 0;20}3.8.8 set容器排序
set容器默认排序规则为从小到大,如何改变排序规则?
利用仿函数,可以改变排序规则。
示例一 set存放内置数据类型
xxxxxxxxxx501
3class MyCompare 4{5public:6 bool operator()(int v1, int v2) 7 {8 return v1 > v2;9 }10};11
12void test01() 13{ 14 set<int> s1;15 s1.insert(10);16 s1.insert(40);17 s1.insert(20);18 s1.insert(30);19 s1.insert(50);20
21 //默认从小到大22 for (set<int>::iterator it = s1.begin(); it != s1.end(); it++) 23 {24 cout << *it << " ";25 }26 cout << endl;27
28 //指定排序规则29 set<int,MyCompare> s2;30 s2.insert(10);31 s2.insert(40);32 s2.insert(20);33 s2.insert(30);34 s2.insert(50);35
36 for (set<int, MyCompare>::iterator it = s2.begin(); it != s2.end(); it++) 37 {38 cout << *it << " ";39 }40 cout << endl;41}42
43int main() 44{45 test01();46
47 system("pause");48
49 return 0;50}总结:利用仿函数可以指定set容器的排序规则。
示例二 set存放自定义数据类型
xxxxxxxxxx551
4class Person5{6public:7 Person(string name, int age)8 {9 this->m_Name = name;10 this->m_Age = age;11 }12
13 string m_Name;14 int m_Age;15};16
17class comparePerson18{19public:20 bool operator()(const Person& p1, const Person &p2)21 {22 //按照年龄进行排序降序23 return p1.m_Age > p2.m_Age;24 }25};26
27void test01()28{29 set<Person, comparePerson> s;30
31 //对于自定义数据类型,set必须指定排序规则才可以插入数据,否则在插的时候就会报错32 Person p1("刘备", 23);33 Person p2("关羽", 27);34 Person p3("张飞", 25);35 Person p4("赵云", 21);36
37 s.insert(p1);38 s.insert(p2);39 s.insert(p3);40 s.insert(p4);41
42 for (set<Person, comparePerson>::iterator it = s.begin(); it != s.end(); it++)43 {44 cout << "姓名: " << it->m_Name << " 年龄: " << it->m_Age << endl;45 }46}47
48int main() 49{50 test01();51
52 system("pause");53
54 return 0;55}总结:对于自定义数据类型,set必须指定排序规则才可以插入数据。
3.9 map/multimap容器
3.9.1 map基本概念
简介:
- map中所有元素都是pair
- pair中第一个元素为key(键值),起到索引作用,第二个元素为value(实值)
- 所有元素都会根据元素的键值自动排序
本质:map/multimap属于关联式容器,底层结构是用二叉树实现。
优点:可以根据key值快速找到value值
map和multimap区别:
- map不允许容器中有重复key值元素,注意value值可以重复
- multimap允许容器中有重复key值元素
3.9.2 map构造和赋值
功能描述:对map容器进行构造和赋值操作
函数原型:
构造:
map<T1, T2> mp;map默认构造函数:map(const map &mp);拷贝构造函数
赋值:
map& operator=(const map &mp);重载等号操作符
示例如下:
xxxxxxxxxx351
3void printMap(map<int,int>&m)4{5 for (map<int, int>::iterator it = m.begin(); it != m.end(); it++)6 {7 cout << "key = " << (*it).first << " value = " << it->second << endl;8 }9 cout << endl;10}11
12void test01()13{14 map<int,int>m; //默认构造15 m.insert(pair<int, int>(1, 10)); //匿名对组16 m.insert(pair<int, int>(2, 20));17 m.insert(pair<int, int>(3, 30));18 printMap(m);19
20 map<int, int>m2(m); //拷贝构造21 printMap(m2);22
23 map<int, int>m3;24 m3 = m2; //赋值25 printMap(m3);26}27
28int main() 29{30 test01();31
32 system("pause");33
34 return 0;35}总结:map中所有元素都是成对出现,插入数据时候要使用对组。
3.9.3 map大小和交换
功能描述:统计map容器大小以及交换map容器
函数原型:
size();返回容器中元素的数目empty();判断容器是否为空swap(st);交换两个集合容器
示例如下:
xxxxxxxxxx631
3void printMap(map<int,int>&m)4{5 for (map<int, int>::iterator it = m.begin(); it != m.end(); it++)6 {7 cout << "key = " << it->first << " value = " << it->second << endl;8 }9 cout << endl;10}11
12void test01()13{14 map<int, int>m;15 m.insert(pair<int, int>(1, 10));16 m.insert(pair<int, int>(2, 20));17 m.insert(pair<int, int>(3, 30));18
19 if (m.empty())20 {21 cout << "m为空" << endl;22 }23 else24 {25 cout << "m不为空" << endl;26 cout << "m的大小为: " << m.size() << endl;27 }28}29
30
31//交换32void test02()33{34 map<int, int>m;35 m.insert(pair<int, int>(1, 10));36 m.insert(pair<int, int>(2, 20));37 m.insert(pair<int, int>(3, 30));38
39 map<int, int>m2;40 m2.insert(pair<int, int>(4, 100));41 m2.insert(pair<int, int>(5, 200));42 m2.insert(pair<int, int>(6, 300));43
44 cout << "交换前" << endl;45 printMap(m);46 printMap(m2);47
48 cout << "交换后" << endl;49 m.swap(m2);50 printMap(m);51 printMap(m2);52}53
54int main() 55{56 test01();57
58 test02();59
60 system("pause");61
62 return 0;63}3.9.4 map插入和删除
功能描述:map容器进行插入数据和删除数据
函数原型:
insert(elem);在容器中插入元素。clear();清除所有元素erase(pos);删除pos迭代器所指的元素,返回下一个元素的迭代器。erase(beg, end);删除区间[beg,end)的所有元素 ,返回下一个元素的迭代器。erase(key);删除容器中值为key的元素。
示例如下:
xxxxxxxxxx501
3void printMap(map<int,int>&m)4{5 for (map<int, int>::iterator it = m.begin(); it != m.end(); it++)6 {7 cout << "key = " << it->first << " value = " << it->second << endl;8 }9 cout << endl;10}11
12void test01()13{14 //插入15 map<int, int> m;16 //第一种插入方式17 m.insert(pair<int, int>(1, 10));18 //第二种插入方式19 m.insert(make_pair(2, 20)); //我猜这个make_pair()是一个函数模板20 //第三种插入方式,复杂不建议使用21 m.insert(map<int, int>::value_type(3, 30));22 //第四种插入方式23 m[4] = 40; 24 printMap(m);25
26 //cout << m[5] << endl;不会报错27 //如果试图访问一个不存在的键,会创建新的键值对,默认值为028 //所以通过重载的[]去访问map容器中的元素要注意键,以免误创建29 30 //删除31 m.erase(m.begin());32 printMap(m);33
34 m.erase(3);35 printMap(m);36
37 //清空38 m.erase(m.begin(),m.end());39 m.clear();40 printMap(m);41}42
43int main() 44{45 test01();46
47 system("pause");48
49 return 0;50}3.9.5 map查找和统计
功能描述:对map容器进行查找数据以及统计数据
函数原型:
find(key);查找key是否存在,若存在,返回该键的元素的迭代器;若不存在,返回set.end();count(key);统计key的元素个数
示例如下:
xxxxxxxxxx351
3//查找和统计4void test01()5{6 map<int, int>m; 7 m.insert(pair<int, int>(1, 10));8 m.insert(pair<int, int>(2, 20));9 m.insert(pair<int, int>(3, 30));10
11 //查找12 map<int, int>::iterator pos = m.find(3);13
14 if (pos != m.end())15 {16 cout << "找到了元素 key = " << (*pos).first << " value = " << (*pos).second << endl;17 }18 else19 {20 cout << "未找到元素" << endl;21 }22
23 //统计24 int num = m.count(3);25 cout << "num = " << num << endl;26}27
28int main() 29{30 test01();31
32 system("pause");33
34 return 0;35}3.9.6 map容器排序
map容器默认排序规则为 按照key值进行 从小到大排序,如何改变排序规则?
利用仿函数,可以改变排序规则
示例如下:
xxxxxxxxxx361
3class MyCompare 4{5public:6 bool operator()(int v1, int v2) 7 {8 return v1 > v2;9 }10};11
12void test01() 13{14 //默认从小到大排序15 //利用仿函数实现从大到小排序16 map<int, int, MyCompare> m;17
18 m.insert(make_pair(1, 10));19 m.insert(make_pair(2, 20));20 m.insert(make_pair(3, 30));21 m.insert(make_pair(4, 40));22 m.insert(make_pair(5, 50));23
24 for (map<int, int, MyCompare>::iterator it = m.begin(); it != m.end(); it++) 25 {26 cout << "key:" << it->first << " value:" << it->second << endl;27 }28}29int main() 30{31 test01();32
33 system("pause");34
35 return 0;36}总结:
- 利用仿函数可以指定map容器的排序规则
- 对于自定义数据类型,map必须要指定排序规则,同set容器
3.10 案例-员工分组
3.10.1 案例描述
- 公司今天招聘了10个员工(ABCDEFGHIJ),10名员工进入公司之后,需要指派员工在那个部门工作
- 员工信息有: 姓名 工资组成;部门分为:策划、美术、研发
- 随机给10名员工分配部门和工资
- 通过multimap进行信息的插入 key(部门编号) value(员工)
- 分部门显示员工信息
3.10.2 实现步骤
- 创建10名员工,放到vector中
- 遍历vector容器,取出每个员工,进行随机分组
- 分组后,将员工部门编号作为key,具体员工作为value,放入到multimap容器中
- 分部门显示员工信息
案例代码:
xxxxxxxxxx1111using namespace std;3
8/*9- 公司今天招聘了10个员工(ABCDEFGHIJ),10名员工进入公司之后,需要指派员工在那个部门工作10- 员工信息有: 姓名 工资组成;部门分为:策划、美术、研发11- 随机给10名员工分配部门和工资12- 通过multimap进行信息的插入 key(部门编号) value(员工)13- 分部门显示员工信息14*/15
16
20class Worker21{22public:23 string m_Name;24 int m_Salary;25};26
27void createWorker(vector<Worker>&v)28{29 string nameSeed = "ABCDEFGHIJ";30 for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++)31 {32 Worker worker;33 worker.m_Name = "员工";34 worker.m_Name += nameSeed[i];35
36 worker.m_Salary = rand() % 10000 + 10000; // 10000 ~ 1999937 //将员工放入到容器中38 v.push_back(worker);39 }40}41
42//员工分组43void setGroup(vector<Worker>&v,multimap<int,Worker>&m)44{45 for (vector<Worker>::iterator it = v.begin(); it != v.end(); it++)46 {47 //产生随机部门编号48 int deptId = rand() % 3; // 0 1 2 49
50 //将员工插入到分组中51 //key部门编号,value具体员工52 m.insert(make_pair(deptId, *it));53 }54}55
56void showWorkerByGourp(multimap<int,Worker>&m)57{58 cout << "策划部门:" << endl;59 multimap<int,Worker>::iterator pos = m.find(CEHUA);60 int count = m.count(CEHUA); // 统计具体人数61 int index = 0;62 for (; pos != m.end() && index < count; pos++ , index++)63 {64 cout << "姓名: " << pos->second.m_Name << " 工资: " << pos->second.m_Salary << endl;65 }66
67 cout << "美术部门: " << endl;68 pos = m.find(MEISHU);69 count = m.count(MEISHU); // 统计具体人数70 index = 0;71 for (; pos != m.end() && index < count; pos++, index++)72 {73 cout << "姓名: " << pos->second.m_Name << " 工资: " << pos->second.m_Salary << endl;74 }75
76 cout << "研发部门: " << endl;77 pos = m.find(YANFA);78 count = m.count(YANFA); // 统计具体人数79 index = 0;80 for (; pos != m.end() && index < count; pos++, index++)81 {82 cout << "姓名: " << pos->second.m_Name << " 工资: " << pos->second.m_Salary << endl;83 }84
85}86
87int main() 88{89 srand((unsigned int)time(NULL));90
91 //1.创建员工92 vector<Worker>vWorker;93 createWorker(vWorker);94
95 //2.员工分组96 multimap<int, Worker>mWorker;97 setGroup(vWorker, mWorker);98
99 //3.分组显示员工100 showWorkerByGourp(mWorker);101
102 ////测试103 //for (vector<Worker>::iterator it = vWorker.begin(); it != vWorker.end(); it++)104 //{105 // cout << "姓名: " << it->m_Name << " 工资: " << it->m_Salary << endl;106 //}107
108 system("pause");109
110 return 0;111}总结:当数据以键值对形式存在,可以考虑用map 或 multimap。
4 STL- 函数对象
4.1 函数对象
4.1.1 函数对象概念
概念:
- 重载函数调用操作符的类,其对象常称为函数对象
- 函数对象使用重载的()时,行为类似函数调用,也叫仿函数
本质:
函数对象(仿函数)是一个类,不是一个函数
4.1.2 函数对象使用
特点:
- 函数对象在使用时,可以像普通函数那样调用, 可以有参数,可以有返回值
- 函数对象超出普通函数的概念,函数对象可以有自己的状态
- 函数对象可以作为参数传递
示例如下:
xxxxxxxxxx661
3//1.函数对象在使用时,可以像普通函数那样调用, 可以有参数,可以有返回值4class MyAdd5{6public :7 int operator()(int v1,int v2)8 {9 return v1 + v2;10 }11};12
13void test01()14{15 MyAdd myAdd;16 cout << myAdd(10, 10) << endl;17}18
19//2.函数对象可以有自己的状态20class MyPrint21{22public:23 MyPrint()24 {25 count = 0;26 }27 void operator()(string test)28 {29 cout << test << endl;30 count++; //统计使用次数31 }32
33 int count; //内部自己的状态34};35
36void test02()37{38 MyPrint myPrint;39 myPrint("hello world");40 myPrint("hello world");41 myPrint("hello world");42 cout << "myPrint调用次数为: " << myPrint.count << endl;43}44
45//3.函数对象可以作为参数传递46void doPrint(MyPrint &mp , string test)47{48 mp(test);49}50
51void test03()52{53 MyPrint myPrint;54 doPrint(myPrint, "Hello C++");55}56
57int main() 58{59 test01();60 test02();61 test03();62
63 system("pause");64
65 return 0;66}4.2 谓词
4.2.1 谓词概念
概念:
- 返回bool类型的仿函数称为谓词
- 如果operator()接受一个参数,那么叫做一元谓词
- 如果operator()接受两个参数,那么叫做二元谓词
4.2.2 一元谓词
示例如下:
xxxxxxxxxx401
4//1.一元谓词5class GreaterFive6{7 bool operator()(int val) 8 {9 return val > 5;10 }11};12
13void test01() 14{15 vector<int> v;16 for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++)17 {18 v.push_back(i);19 }20
21 //传入的GreaterFive()是一个匿名对象22 vector<int>::iterator it = find_if(v.begin(), v.end(), GreaterFive());23 if (it == v.end()) 24 {25 cout << "没找到!" << endl;26 }27 else {28 cout << "找到:" << *it << endl;29 }30
31}32
33int main() 34{35 test01();36
37 system("pause");38
39 return 0;40}4.2.3 二元谓词
示例如下:
xxxxxxxxxx471
4//二元谓词5class MyCompare6{7public:8 bool operator()(int num1, int num2)9 {10 return num1 > num2;11 }12};13
14void test01()15{16 vector<int> v;17 v.push_back(10);18 v.push_back(40);19 v.push_back(20);20 v.push_back(30);21 v.push_back(50);22
23 //默认从小到大24 sort(v.begin(), v.end());25 for (vector<int>::iterator it = v.begin(); it != v.end(); it++)26 {27 cout << *it << " ";28 }29 cout << endl;30
31 //使用函数对象改变算法策略,排序从大到小32 sort(v.begin(), v.end(), MyCompare());33 for (vector<int>::iterator it = v.begin(); it != v.end(); it++)34 {35 cout << *it << " ";36 }37 cout << endl;38}39
40int main() 41{42 test01();43
44 system("pause");45
46 return 0;47}总结:前面已经有好多改变算法策略的做法,这里做一个小结。List排序,使用成员函数L.sort(),里面传入一个bool返回值的全局函数名来指定算法策略。set和map在容器初始化的时候就指定算法策略,例如:set<int,MyCompare> s2;、map<int, int, MyCompare> m;其中MyCompare是仿函数类名。而标准算法库下的sort()以及find_if()都是传入仿函数的匿名对象。
4.3 内建函数对象
4.3.1 内建函数对象意义
概念:STL内建了一些函数对象
分类:
- 算术仿函数
- 关系仿函数
- 逻辑仿函数
用法:
- 这些仿函数所产生的对象,用法和一般函数完全相同
- 使用内建函数对象,需要引入头文件
#include<functional>
4.3.2 算术仿函数
功能描述:
- 实现四则运算
- 其中negate是一元运算,其他都是二元运算
仿函数原型:
template<class T> T plus<T>加法仿函数template<class T> T minus<T>减法仿函数template<class T> T multiplies<T>乘法仿函数template<class T> T divides<T>除法仿函数template<class T> T modulus<T>取模仿函数template<class T> T negate<T>取相反数仿函数
示例如下:
xxxxxxxxxx251
3//negate4void test01()5{6 negate<int> n;7 cout << n(50) << endl;8}9
10//plus11void test02()12{13 plus<int> p;14 cout << p(10, 20) << endl;15}16
17int main() 18{19 test01();20 test02();21
22 system("pause");23
24 return 0;25}注意:使用内建函数对象时,需要引入头文件 #include <functional>。
4.3.3 关系仿函数
功能描述:实现关系对比
仿函数原型:
template<class T> bool equal_to<T>等于template<class T> bool not_equal_to<T>不等于template<class T> bool greater<T>大于template<class T> bool greater_equal<T>大于等于template<class T> bool less<T>小于template<class T> bool less_equal<T>小于等于
示例如下:
xxxxxxxxxx491
5class MyCompare6{7public:8 bool operator()(int v1,int v2)9 {10 return v1 > v2;11 }12};13
14void test01()15{16 vector<int> v;17
18 v.push_back(10);19 v.push_back(30);20 v.push_back(50);21 v.push_back(40);22 v.push_back(20);23
24 for (vector<int>::iterator it = v.begin(); it != v.end(); it++) 25 {26 cout << *it << " ";27 }28 cout << endl;29
30 //自己实现仿函数31 //sort(v.begin(), v.end(), MyCompare());32 //STL内建仿函数,大于仿函数33 sort(v.begin(), v.end(), greater<int>());34
35 for (vector<int>::iterator it = v.begin(); it != v.end(); it++) 36 {37 cout << *it << " ";38 }39 cout << endl;40}41
42int main() 43{44 test01();45
46 system("pause");47
48 return 0;49}总结:关系仿函数中最常用的就是greater<>大于,常用于改变算法策略。
4.3.4 逻辑仿函数
功能描述:实现逻辑运算
函数原型:
template<class T> bool logical_and<T>逻辑与template<class T> bool logical_or<T>逻辑或template<class T> bool logical_not<T>逻辑非
示例如下:
xxxxxxxxxx381
5void test01()6{7 vector<bool> v;8 v.push_back(true);9 v.push_back(false);10 v.push_back(true);11 v.push_back(false);12
13 for (vector<bool>::iterator it = v.begin();it!= v.end();it++)14 {15 cout << *it << " ";16 }17 cout << endl;18
19 //逻辑非,将v容器搬运到v2中,并执行逻辑非运算20 vector<bool> v2;21 //必须提前扩展容器的容量,否则搬不进去报错!22 v2.resize(v.size());23 transform(v.begin(), v.end(), v2.begin(), logical_not<bool>());24 for (vector<bool>::iterator it = v2.begin(); it != v2.end(); it++)25 {26 cout << *it << " ";27 }28 cout << endl;29}30
31int main() 32{33 test01();34
35 system("pause");36
37 return 0;38}5 STL- 常用算法
概述:
- 算法主要是由头文件
<algorithm>、<functional>、<numeric>组成。 <algorithm>是所有STL头文件中最大的一个,范围涉及到比较、 交换、查找、遍历操作、复制、修改等等<numeric>体积很小,只包括几个在序列上面进行简单数学运算的模板函数<functional>定义了一些模板类,用以声明函数对象。
5.1 常用遍历算法
算法简介:
for_each遍历容器transform搬运容器到另一个容器中
5.1.1 for_each
功能描述:实现遍历容器
函数原型:
for_each(iterator beg, iterator end, _func);
遍历算法 遍历容器元素
beg 开始迭代器
end 结束迭代器
_func 函数或者函数对象,普通函数用函数名、仿函数用匿名对象
示例如下:
xxxxxxxxxx441
4//普通函数5void print01(int val) 6{7 cout << val << " ";8}9
10//函数对象11class print02 12{13 public:14 void operator()(int val) 15 {16 cout << val << " ";17 }18};19
20//for_each算法基本用法21void test01() 22{23 vector<int> v;24 for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) 25 {26 v.push_back(i);27 }28
29 //遍历算法30 for_each(v.begin(), v.end(), print01);31 cout << endl;32
33 for_each(v.begin(), v.end(), print02());34 cout << endl;35}36
37int main() 38{39 test01();40
41 system("pause");42
43 return 0;44}总结:for_each是最常用遍历算法,需要熟练掌握。
5.1.2 transform
功能描述:搬运容器到另一个容器中
函数原型:
transform(iterator beg1, iterator end1, iterator beg2, _func);
beg1 源容器开始迭代器
end1 源容器结束迭代器
beg2 目标容器开始迭代器
_func 函数或者函数对象
示例如下:
xxxxxxxxxx461
4//常用遍历算法--搬运transform5
6class TransForm7{8public:9 int operator()(int val)10 {11 return val;12 }13};14
15class MyPrint16{17public:18 void operator()(int val)19 {20 cout << val << " ";21 }22};23
24void test01()25{26 vector<int>v;27 for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++)28 {29 v.push_back(i);30 }31
32 vector<int>vTarget; //目标容器33 vTarget.resize(v.size()); //目标容器需要提前开辟空间34 transform(v.begin(), v.end(), vTarget.begin(), TransForm());35
36 for_each(vTarget.begin(), vTarget.end(), MyPrint());37}38
39int main() 40{41 test01();42
43 system("pause");44
45 return 0;46}总结: 搬运的目标容器必须要提前开辟空间,否则无法正常搬运!搬运不止能进行原模原样的搬运,还能对其进行一些运算操作,再搬到目标容器。
5.2 常用查找算法
算法简介:
find查找元素find_if按条件查找元素adjacent_find查找相邻重复元素binary_search二分查找法count统计元素个数count_if按条件统计元素个数
5.2.1 find
功能描述:查找指定元素,找到返回指定元素的迭代器,找不到返回结束迭代器end()
函数原型:
find(iterator beg, iterator end, value);
按值查找元素,找到返回指定位置迭代器,找不到返回结束迭代器位置
beg 开始迭代器
end 结束迭代器
value 查找的元素
示例如下:
xxxxxxxxxx841
5void test01() 6{7 vector<int> v;8 for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) 9 {10 v.push_back(i + 1);11 }12 13 //查找容器中是否有 5 这个元素14 vector<int>::iterator it = find(v.begin(), v.end(), 5);15 if (it == v.end()) 16 {17 cout << "没有找到!" << endl;18 }19 else 20 {21 cout << "找到:" << *it << endl;22 }23}24
25class Person 26{27public:28 Person(string name, int age) 29 {30 this->m_Name = name;31 this->m_Age = age;32 }33 //重载==34 bool operator==(const Person& p) 35 {36 if (this->m_Name == p.m_Name && this->m_Age == p.m_Age) 37 {38 return true;39 }40 return false;41 }42
43public:44 string m_Name;45 int m_Age;46};47
48void test02() 49{50 vector<Person> v;51
52 //创建数据53 Person p1("aaa", 10);54 Person p2("bbb", 20);55 Person p3("ccc", 30);56 Person p4("ddd", 40);57
58 v.push_back(p1);59 v.push_back(p2);60 v.push_back(p3);61 v.push_back(p4);62
63 Person pp("bbb",20);64 vector<Person>::iterator it = find(v.begin(), v.end(), pp);65 if (it == v.end()) 66 {67 cout << "没有找到!" << endl;68 }69 else 70 {71 cout << "找到姓名:" << it->m_Name << " 年龄: " << it->m_Age << endl;72 }73}74
75int main() 76{77 test01();78 79 test02();80
81 system("pause");82
83 return 0;84}总结: 利用find可以在容器中找指定的元素,返回值是迭代器。
5.2.2 find_if
功能描述:按条件查找元素
函数原型:
find_if(iterator beg, iterator end, _Pred);
按值查找元素,找到返回指定位置迭代器,找不到返回结束迭代器位置
beg 开始迭代器
end 结束迭代器
_Pred 函数或者谓词(返回bool类型的仿函数)
示例如下:
xxxxxxxxxx921
5//内置数据类型6class GreaterFive7{8public:9 bool operator()(int val)10 {11 return val > 5;12 }13};14
15void test01() 16{17 vector<int> v;18 for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) 19 {20 v.push_back(i + 1);21 }22
23 vector<int>::iterator it = find_if(v.begin(), v.end(), GreaterFive());24 if (it == v.end()) 25 {26 cout << "没有找到!" << endl;27 }28 else {29 cout << "找到大于5的数字:" << *it << endl;30 }31}32
33//自定义数据类型34class Person 35{36public:37 Person(string name, int age)38 {39 this->m_Name = name;40 this->m_Age = age;41 }42public:43 string m_Name;44 int m_Age;45};46
47class Greater2048{49public:50 bool operator()(Person &p)51 {52 return p.m_Age > 20;53 }54
55};56
57void test02() 58{59 vector<Person> v;60
61 //创建数据62 Person p1("aaa", 10);63 Person p2("bbb", 20);64 Person p3("ccc", 30);65 Person p4("ddd", 40);66
67 v.push_back(p1);68 v.push_back(p2);69 v.push_back(p3);70 v.push_back(p4);71
72 vector<Person>::iterator it = find_if(v.begin(), v.end(), Greater20());73 if (it == v.end())74 {75 cout << "没有找到!" << endl;76 }77 else78 {79 cout << "找到姓名:" << it->m_Name << " 年龄: " << it->m_Age << endl;80 }81}82
83int main() 84{85 test01();86
87 test02();88
89 system("pause");90
91 return 0;92}总结:find_if按条件查找使查找更加灵活,提供的仿函数可以改变不同的策略。
5.2.3 adjacent_find
功能描述:查找相邻重复元素
函数原型:
adjacent_find(iterator beg, iterator end);
查找相邻重复元素,返回相邻元素的第一个位置的迭代器
beg 开始迭代器
end 结束迭代器
示例如下:
xxxxxxxxxx251
4void test01()5{6 vector<int> v;7 v.push_back(1);8 v.push_back(2);9 v.push_back(5);10 v.push_back(2);11 v.push_back(4);12 v.push_back(4);13 v.push_back(3);14
15 //查找相邻重复元素16 vector<int>::iterator it = adjacent_find(v.begin(), v.end());17 if (it == v.end()) 18 {19 cout << "找不到!" << endl;20 }21 else 22 {23 cout << "找到相邻重复元素为:" << *it << endl;24 }25}总结:这个算法不常用,但是如果用到要记得,省的自己写函数。
5.2.4 binary_search(二分查找)
功能描述:查找指定元素是否存在
函数原型:
bool binary_search(iterator beg, iterator end, value);
查找指定的元素,查到 返回true 否则false
注意: 在无序序列中不可用
beg 开始迭代器
end 结束迭代器
value 查找的元素
示例如下:
xxxxxxxxxx321
4void test01()5{6 vector<int>v;7
8 for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++)9 {10 v.push_back(i);11 }12 13 //二分查找14 bool ret = binary_search(v.begin(), v.end(),2);15 if (ret)16 {17 cout << "找到了" << endl;18 }19 else20 {21 cout << "未找到" << endl;22 }23}24
25int main() 26{27 test01();28
29 system("pause");30
31 return 0;32}总结:二分查找法查找效率很高,值得注意的是查找的容器中元素必须的有序序列,如果无序,结果可能有误!
5.2.5 count
功能描述:统计元素个数
函数原型:
count(iterator beg, iterator end, value);
统计元素出现次数
beg 开始迭代器
end 结束迭代器
value 统计的元素
示例如下:
xxxxxxxxxx761
4//内置数据类型5void test01()6{7 vector<int> v;8 v.push_back(1);9 v.push_back(2);10 v.push_back(4);11 v.push_back(5);12 v.push_back(3);13 v.push_back(4);14 v.push_back(4);15
16 int num = count(v.begin(), v.end(), 4);17
18 cout << "4的个数为: " << num << endl;19}20
21//自定义数据类型22class Person23{24public:25 Person(string name, int age)26 {27 this->m_Name = name;28 this->m_Age = age;29 }30 bool operator==(const Person & p)31 {32 if (this->m_Age == p.m_Age)33 {34 return true;35 }36 else37 {38 return false;39 }40 }41 string m_Name;42 int m_Age;43};44
45void test02()46{47 vector<Person> v;48
49 Person p1("刘备", 35);50 Person p2("关羽", 35);51 Person p3("张飞", 35);52 Person p4("赵云", 30);53 Person p5("曹操", 25);54
55 v.push_back(p1);56 v.push_back(p2);57 v.push_back(p3);58 v.push_back(p4);59 v.push_back(p5);60 61 Person p("诸葛亮",35);62
63 int num = count(v.begin(), v.end(), p);64 cout << "num = " << num << endl;65}66
67int main() 68{69 test01();70
71 test02();72
73 system("pause");74
75 return 0;76}总结: 统计自定义数据类型时候,需要配合重载 operator==。
5.2.6 count_if
功能描述:按条件统计元素个数
函数原型:
count_if(iterator beg, iterator end, _Pred);
按条件统计元素出现次数
beg 开始迭代器
end 结束迭代器
_Pred 谓词(返回bool类型的仿函数),以匿名对象的方式传入
示例如下:
xxxxxxxxxx811
4class Greater45{6public:7 bool operator()(int val)8 {9 return val >= 4;10 }11};12
13//内置数据类型14void test01()15{16 vector<int> v;17 v.push_back(1);18 v.push_back(2);19 v.push_back(4);20 v.push_back(5);21 v.push_back(3);22 v.push_back(4);23 v.push_back(4);24
25 int num = count_if(v.begin(), v.end(), Greater4());26
27 cout << "大于4的个数为: " << num << endl;28}29
30//自定义数据类型31class Person32{33public:34 Person(string name, int age)35 {36 this->m_Name = name;37 this->m_Age = age;38 }39
40 string m_Name;41 int m_Age;42};43
44class AgeLess3545{46public:47 bool operator()(const Person &p)48 {49 return p.m_Age < 35;50 }51};52void test02()53{54 vector<Person> v;55
56 Person p1("刘备", 35);57 Person p2("关羽", 35);58 Person p3("张飞", 35);59 Person p4("赵云", 30);60 Person p5("曹操", 25);61
62 v.push_back(p1);63 v.push_back(p2);64 v.push_back(p3);65 v.push_back(p4);66 v.push_back(p5);67
68 int num = count_if(v.begin(), v.end(), AgeLess35());69 cout << "小于35岁的个数:" << num << endl;70}71
72int main() 73{74 test01();75
76 test02();77
78 system("pause");79
80 return 0;81}总结:按值统计用count,按条件统计用count_if。
5.3 常用排序算法
算法简介:
sort对容器内元素进行排序random_shuffle洗牌 指定范围内的元素随机调整次序merge容器元素合并,并存储到另一容器中reverse反转指定范围的元素
5.3.1 sort
功能描述:对容器内元素进行排序
函数原型:
sort(iterator beg, iterator end, _Pred);
按值查找元素,找到返回指定位置迭代器,找不到返回结束迭代器位置
beg 开始迭代器
end 结束迭代器
_Pred 谓词,用来指定特殊的排序规则
示例如下:
xxxxxxxxxx361
4void myPrint(int val)5{6 cout << val << " ";7}8
9void test01() 10{11 vector<int> v;12 v.push_back(10);13 v.push_back(30);14 v.push_back(50);15 v.push_back(20);16 v.push_back(40);17
18 //sort默认从小到大排序19 sort(v.begin(), v.end());20 for_each(v.begin(), v.end(), myPrint);21 cout << endl;22
23 //从大到小排序24 sort(v.begin(), v.end(), greater<int>());25 for_each(v.begin(), v.end(), myPrint);26 cout << endl;27}28
29int main() 30{31 test01();32
33 system("pause");34
35 return 0;36}总结:sort属于开发中最常用的算法之一,需熟练掌握。
5.3.2 random_shuffle
功能描述:洗牌 指定范围内的元素随机调整次序
函数原型:
random_shuffle(iterator beg, iterator end);
指定范围内的元素随机调整次序
beg 开始迭代器
end 结束迭代器
示例如下:
xxxxxxxxxx401
5class myPrint6{7public:8 void operator()(int val)9 {10 cout << val << " ";11 }12};13
14void test01()15{16 //设置随机数种子17 srand((unsigned int)time(NULL));18 19 vector<int> v;20 for(int i = 0 ; i < 10;i++)21 {22 v.push_back(i);23 }24 for_each(v.begin(), v.end(), myPrint());25 cout << endl;26
27 //打乱顺序28 random_shuffle(v.begin(), v.end());29 for_each(v.begin(), v.end(), myPrint());30 cout << endl;31}32
33int main() 34{35 test01();36
37 system("pause");38
39 return 0;40}总结:random_shuffle洗牌算法比较实用,使用时记得加随机数种子。
5.3.3 merge
功能描述:两个容器元素合并,并存储到另一容器中
函数原型:
merge(iterator beg1, iterator end1, iterator beg2, iterator end2, iterator dest);
容器元素合并,并存储到另一容器中
注意:两个容器必须是有序的,合并出的目标容器也是有序的,有点分组排序降低复杂度的味道
beg1 容器1开始迭代器
end1 容器1结束迭代器
beg2 容器2开始迭代器
end2 容器2结束迭代器
dest 目标容器开始迭代器
示例如下:
xxxxxxxxxx391
4class myPrint5{6public:7 void operator()(int val)8 {9 cout << val << " ";10 }11};12
13void test01()14{15 vector<int> v1;16 vector<int> v2;17 for (int i = 0; i < 10 ; i++) 18 {19 v1.push_back(i);20 v2.push_back(i + 1);21 }22
23 vector<int> vtarget;24 //目标容器需要提前开辟空间25 vtarget.resize(v1.size() + v2.size());26 //合并,需要两个有序序列27 merge(v1.begin(), v1.end(), v2.begin(), v2.end(), vtarget.begin());28 for_each(vtarget.begin(), vtarget.end(), myPrint());29 cout << endl;30}31
32int main() 33{34 test01();35
36 system("pause");37
38 return 0;39}总结:merge合并的两个容器必须的有序序列。
5.3.4 reverse
功能描述:将容器内元素进行反转
函数原型:
reverse(iterator beg, iterator end);
反转指定范围的元素
beg 开始迭代器
end 结束迭代器
示例如下:
xxxxxxxxxx401
4class myPrint5{6public:7 void operator()(int val)8 {9 cout << val << " ";10 }11};12
13void test01()14{15 vector<int> v;16 v.push_back(10);17 v.push_back(30);18 v.push_back(50);19 v.push_back(20);20 v.push_back(40);21
22 cout << "反转前: " << endl;23 for_each(v.begin(), v.end(), myPrint());24 cout << endl;25
26 cout << "反转后: " << endl;27
28 reverse(v.begin(), v.end());29 for_each(v.begin(), v.end(), myPrint());30 cout << endl;31}32
33int main() 34{35 test01();36
37 system("pause");38
39 return 0;40}5.4 常用拷贝和替换算法
算法简介:
copy容器内指定范围的元素拷贝到另一容器中replace将容器内指定范围的旧元素修改为新元素replace_if容器内指定范围满足条件的元素替换为新元素swap互换两个容器的元素
5.4.1 copy
功能描述:容器内指定范围的元素拷贝到另一容器中
函数原型:
copy(iterator beg, iterator end, iterator dest);
beg 开始迭代器
end 结束迭代器
dest 目标起始迭代器
示例如下:
xxxxxxxxxx371
4class myPrint5{6public:7 void operator()(int val)8 {9 cout << val << " ";10 }11};12
13void test01()14{15 vector<int> v1;16 for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) 17 {18 v1.push_back(i + 1);19 }20 21 vector<int> v2;22 //目标容器提前开辟空间23 v2.resize(v1.size());24 copy(v1.begin(), v1.end(), v2.begin());25
26 for_each(v2.begin(), v2.end(), myPrint());27 cout << endl;28}29
30int main() 31{32 test01();33
34 system("pause");35
36 return 0;37}总结:利用copy算法在拷贝时,目标容器记得提前开辟空间。copy算法用的比较少,直接=赋值简单。
5.4.2 replace
功能描述:将容器内指定范围的旧元素修改为新元素
函数原型:
replace(iterator beg, iterator end, oldvalue, newvalue);
将区间内旧元素 替换成 新元素
beg 开始迭代器
end 结束迭代器
oldvalue 旧元素
newvalue 新元素
示例如下:
xxxxxxxxxx421
4class myPrint5{6public:7 void operator()(int val)8 {9 cout << val << " ";10 }11};12
13void test01()14{15 vector<int> v;16 v.push_back(20);17 v.push_back(30);18 v.push_back(20);19 v.push_back(40);20 v.push_back(50);21 v.push_back(10);22 v.push_back(20);23
24 cout << "替换前:" << endl;25 for_each(v.begin(), v.end(), myPrint());26 cout << endl;27
28 //将容器中的20 替换成 200029 cout << "替换后:" << endl;30 replace(v.begin(), v.end(), 20,2000);31 for_each(v.begin(), v.end(), myPrint());32 cout << endl;33}34
35int main() 36{37 test01();38
39 system("pause");40
41 return 0;42}5.4.3 replace_if
功能描述: 将区间内满足条件的元素,替换成指定元素
函数原型:
replace_if(iterator beg, iterator end, _pred, newvalue);
按条件替换元素,满足条件的替换成指定元素
beg 开始迭代器
end 结束迭代器
_pred 谓词
newvalue 替换的新元素
示例如下:
xxxxxxxxxx521
4class myPrint5{6public:7 void operator()(int val)8 {9 cout << val << " ";10 }11};12
13class ReplaceGreater3014{15public:16 bool operator()(int val)17 {18 return val >= 30;19 }20
21};22
23void test01()24{25 vector<int> v;26 v.push_back(20);27 v.push_back(30);28 v.push_back(20);29 v.push_back(40);30 v.push_back(50);31 v.push_back(10);32 v.push_back(20);33
34 cout << "替换前:" << endl;35 for_each(v.begin(), v.end(), myPrint());36 cout << endl;37
38 //将容器中大于等于的30 替换成 300039 cout << "替换后:" << endl;40 replace_if(v.begin(), v.end(), ReplaceGreater30(), 3000);41 for_each(v.begin(), v.end(), myPrint());42 cout << endl;43}44
45int main() 46{47 test01();48
49 system("pause");50
51 return 0;52}总结:replace_if按条件查找,可以利用仿函数灵活筛选满足的条件。
5.4.4 swap
功能描述:互换两个容器的元素
函数原型:
swap(container c1, container c2);
互换两个容器的元素,两个容器必须是同种类型
c1容器1
c2容器2
示例如下:
xxxxxxxxxx441
4class myPrint5{6public:7 void operator()(int val)8 {9 cout << val << " ";10 }11};12
13void test01()14{15 vector<int> v1;16 vector<int> v2;17 for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) 18 {19 v1.push_back(i);20 v2.push_back(i+100);21 }22
23 cout << "交换前: " << endl;24 for_each(v1.begin(), v1.end(), myPrint());25 cout << endl;26 for_each(v2.begin(), v2.end(), myPrint());27 cout << endl;28
29 cout << "交换后: " << endl;30 swap(v1, v2);31 for_each(v1.begin(), v1.end(), myPrint());32 cout << endl;33 for_each(v2.begin(), v2.end(), myPrint());34 cout << endl;35}36
37int main() 38{39 test01();40
41 system("pause");42
43 return 0;44}总结:swap交换容器时,注意交换的容器要同种类型。
5.5 常用算术生成算法
注意:算术生成算法属于小型算法,使用时包含的头文件为 #include <numeric>
算法简介:
accumulate计算容器元素累计总和fill向容器中添加元素
5.5.1 accumulate
功能描述:计算区间内 容器元素累计总和
函数原型:
accumulate(iterator beg, iterator end, value);
计算容器元素累计总和
beg 开始迭代器
end 结束迭代器
value 起始值
示例如下:
xxxxxxxxxx241
4void test01()5{6 vector<int> v;7 for (int i = 0; i <= 100; i++) 8 {9 v.push_back(i);10 }11
12 int total = accumulate(v.begin(), v.end(), 0);13
14 cout << "total = " << total << endl;15}16
17int main() 18{19 test01();20
21 system("pause");22
23 return 0;24}总结:accumulate使用时头文件注意是 numeric,这个算法很实用。
5.5.2 fill
功能描述:向容器中填充指定的元素
函数原型:
fill(iterator beg, iterator end, value);
向容器中填充元素
beg 开始迭代器
end 结束迭代器
value 填充的值
示例如下:
xxxxxxxxxx321
5class myPrint6{7public:8 void operator()(int val)9 {10 cout << val << " ";11 }12};13
14void test01()15{16 vector<int> v;17 v.resize(10);18 //填充19 fill(v.begin(), v.end(), 100);20
21 for_each(v.begin(), v.end(), myPrint());22 cout << endl;23}24
25int main() 26{27 test01();28
29 system("pause");30
31 return 0;32}5.6 常用集合算法
算法简介:
set_intersection求两个容器的交集set_union求两个容器的并集set_difference求两个容器的差集
5.6.1 set_intersection
功能描述:求两个容器的交集
函数原型:
set_intersection(iterator beg1, iterator end1, iterator beg2, iterator end2, iterator dest);
求两个集合的交集
注意:两个集合必须是有序序列
beg1 容器1开始迭代器
end1 容器1结束迭代器
beg2 容器2开始迭代器
end2 容器2结束迭代器
dest 目标容器开始迭代器
示例如下:
xxxxxxxxxx441
4class myPrint5{6public:7 void operator()(int val)8 {9 cout << val << " ";10 }11};12
13void test01()14{15 vector<int> v1;16 vector<int> v2;17 for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++)18 {19 v1.push_back(i);20 v2.push_back(i+5);21 }22
23 vector<int> vTarget;24 25 //取两个里面较小的值给目标容器开辟空间26 vTarget.resize(min(v1.size(), v2.size()));27
28 //返回目标容器的最后一个元素的迭代器地址29 vector<int>::iterator itEnd = 30 set_intersection(v1.begin(), v1.end(), v2.begin(), v2.end(), vTarget.begin());31
32 //遍历的时候用itEnd,否则把容器全遍历出来,包括后面补充的033 for_each(vTarget.begin(), itEnd, myPrint());34 cout << endl;35}36
37int main() 38{39 test01();40
41 system("pause");42
43 return 0;44}总结:
- 求交集的两个集合必须是有序序列
- 目标容器开辟空间需要从两个容器中取小值
- set_intersection返回值是所求交集中最后一个元素的位置
5.6.2 set_union
功能描述:求两个集合的并集
函数原型:
set_union(iterator beg1, iterator end1, iterator beg2, iterator end2, iterator dest);
求两个集合的并集
注意:两个集合必须是有序序列
beg1 容器1开始迭代器
end1 容器1结束迭代器
beg2 容器2开始迭代器
end2 容器2结束迭代器
dest 目标容器开始迭代器
示例如下:
xxxxxxxxxx421
4class myPrint5{6public:7 void operator()(int val)8 {9 cout << val << " ";10 }11};12
13void test01()14{15 vector<int> v1;16 vector<int> v2;17 for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) 18 {19 v1.push_back(i);20 v2.push_back(i+5);21 }22
23 vector<int> vTarget;24 //取两个容器的和给目标容器开辟空间25 vTarget.resize(v1.size() + v2.size());26
27 //返回目标容器的最后一个元素的迭代器地址28 vector<int>::iterator itEnd = 29 set_union(v1.begin(), v1.end(), v2.begin(), v2.end(), vTarget.begin());30
31 for_each(vTarget.begin(), itEnd, myPrint());32 cout << endl;33}34
35int main() 36{37 test01();38
39 system("pause");40
41 return 0;42}总结:
- 求并集的两个集合必须是有序序列
- 目标容器开辟空间需要两个容器相加
- set_union返回值是所求并集中最后一个元素的位置
5.6.3 set_difference
功能描述:求两个集合的差集
函数原型:
set_difference(iterator beg1, iterator end1, iterator beg2, iterator end2, iterator dest);
求两个集合的差集
注意:两个集合必须是有序序列
beg1 容器1开始迭代器
end1 容器1结束迭代器
beg2 容器2开始迭代器
end2 容器2结束迭代器
dest 目标容器开始迭代器
示例如下:
xxxxxxxxxx481
4class myPrint5{6public:7 void operator()(int val)8 {9 cout << val << " ";10 }11};12
13void test01()14{15 vector<int> v1;16 vector<int> v2;17 for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) 18 {19 v1.push_back(i);20 v2.push_back(i+5);21 }22
23 vector<int> vTarget;24 25 //取两个里面较大的值给目标容器开辟空间26 vTarget.resize( max(v1.size() , v2.size()));27
28 //返回目标容器的最后一个元素的迭代器地址29 cout << "v1与v2的差集为: " << endl;30 vector<int>::iterator itEnd = 31 set_difference(v1.begin(), v1.end(), v2.begin(), v2.end(), vTarget.begin());32 for_each(vTarget.begin(), itEnd, myPrint());33 cout << endl;34
35 cout << "v2与v1的差集为: " << endl;36 itEnd = set_difference(v2.begin(), v2.end(), v1.begin(), v1.end(), vTarget.begin());37 for_each(vTarget.begin(), itEnd, myPrint());38 cout << endl;39}40
41int main() 42{43 test01();44
45 system("pause");46
47 return 0;48}总结:
- 求差集的两个集合必须是有序序列
- 目标容器开辟空间需要从两个容器取较大值
- set_difference返回值是所求差集中最后一个元素的位置